Corporate Analysis of Lufthansa Group 2017
analysis the financial performance代写 This report is to analyse Lufthansa Group’s year-end performance in 2017 through analysis the financial performance

201109947
12/April/18
Contents
Executive Summary……………………………………………………………………………………….2
Key Highlights ………………………………………………………………………………………………2
1. Introduction ………………………………………………………………………………………………3
2. Financial performance …………………………………………………………………………….3
2.1. Revenue ……………………………………………………………………………………………………3
Figure 1…………………………………………………………………………………………………………….. 4
2.2. Operating margin …………………………………………………………………………………….4
2.3. EBIT and EBITDA margin ………………………………………………………………………..5
2.4. Share price………………………………………………………………………………………………. .5
Figure 2……………………………………………………………………………………………………………… 6
3. Position …………………………………………………………………………………………………………7
3.1. Goodwill and other intangible assets ………………………………………………………7
3.2. Total liability………………………………………………………………………………………………7
3.3. Long-term solvency………………………………………………………………….. …………….8
Figure 3………………………………………………………………………………………………………………..8
4. Liquidity and Cash flow…………………………………………………………………………………9
4.1. Quick ratio………………………………………………………………………………………………….9
Figure 4 ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..10
4.2. Receivable days ………………………………………………………………………………………….10
4.3. Cash from operating activities ……………………………………………………………………11
Figure 5…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………. 12
4.4. Cash from investment activities ………………………………………………………………….12
4.5. CASH ROCE ……………………………………………………………………………………………………13
5. Events after balance…………………………………………………………………………..13
6. Conclusion ………………………………………………………………………………………………………….14
7. Reference …………………………………………………………………………………………………………….14
8. Appendices ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………15
8.1. Operating margin ………………………………………………………………………………………………15
8.2. EBITDA margin …………………………………………………………………………………………………16
8.3. Share price …………………………………………………………………………………………………………16
8.4. Goodwill ……………………………………………………………………………………………………………..17
8.5. Total liabilities ……………………………………………………………………………………………………18
8.6. Receivable days …………………………………………………………………………………………………..18
8.7. Cash from investment activities ………………………………………………………………………..19
Executive Summary analysis the financial performance代写
The aim of this report is to analyse Lufthansa Group’s year-end performance in 2017 through analysis the financial performance, position and liquidity. The main methods of analysis for this report include: revenue, operating margin, EBIT, share price, and liquidity, such as quick ratio and receivable days.
Key Highlights
- Revenue increase 12% to EUR 35.6 billion, operating margin up by 1.2% to 8.8%.
- EBIT was EUR 3.310 billion in 2017, rose by 45.5% compare with 2016.
- Share price rose 150.4% compare with 2016, clear upward trend in 2017.
- Gearing decreased dramatically to 83.4%; interest coverage was 7.84, ranked at second in decade.
- Merely reduced in quick ratio by 0.06 to 0.87.
- Quick ratio and receivable days are both merely reduced. Quick ratio was 0.87, receivable days was 37.43 days.
- Cash return on capital employed was 25.8% which increased 8.4% compare with 2016.
- Acquired remaining 55% share in Brussels Airlines.
- Bankruptcy and partial acquisition of Air Berlin.analysis the financial performance代写
1. Introduction
Lufthansa group is an aviation group with a leading position in the industry. It consists of five main business segments, NETWORK AIRLINES, POINT-TO-POINT AIRLINES, LOGISTICS, MRO, and CATERING. Which mainly rely on Network Airlines, Point-to-Point Airlines to create benefits.
2. Financial performance
2.1. Revenue
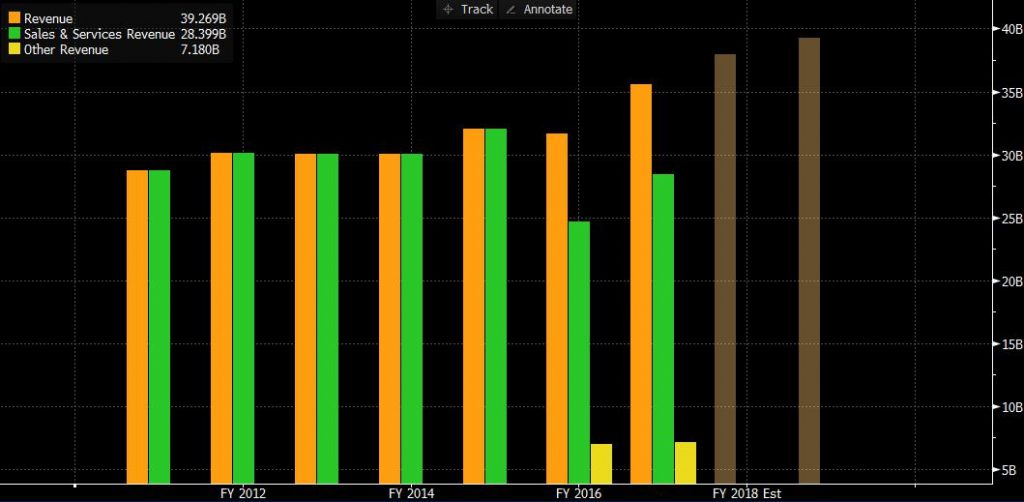
Figure 1
Compared with 2017, revenue increased by approximately 12.4%. It is divided into traffic income and other income. The main course for the increase is traffic income rose to EUR 28.4 billion, compared with 2016 it increase about 15.2%. Customers are still the main component of traffic income. According to statistics, the number of customers in 2017 increased by 18.6% from the previous year to EUR 130 million.
This increase was mainly due to the acquisition of 55% of Brussels Airlines on January 9, 2017. Another important reason is that Air Berlin, the second largest airline in Germany, declared bankruptcy in August 2017. In the fourth quarter of 2017, due to Air Berlin, increased revenue by EUR 150 million. With the continuous development of the global economy, the demand of the aviation industry in various regions has continuously increased. As the International Air Transport Association pointed out, the number of passenger kilometres in revenue increased by 7.6% in 2017. The average price has risen, and thus brought in most of the income. (Investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com, 2018)
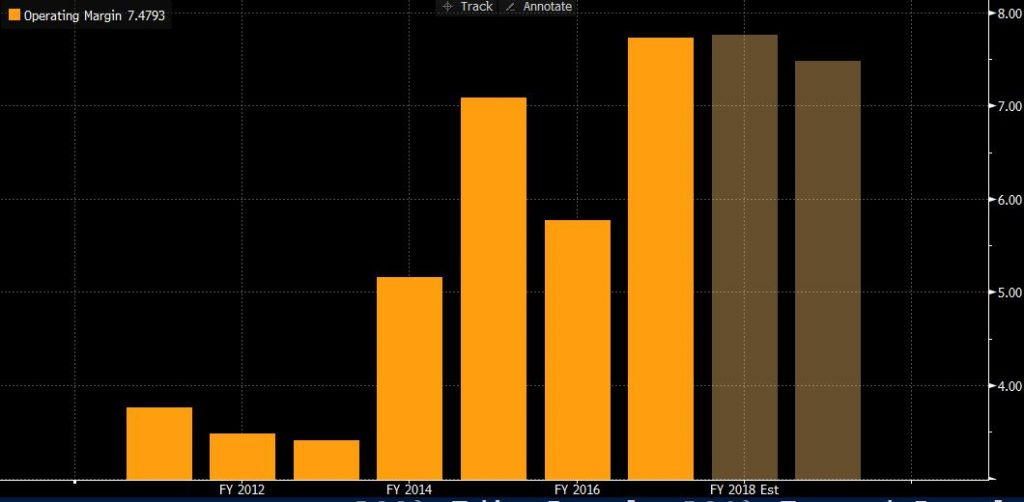
2.2. Operating margin
In 2017, Lufthansa’s operating margin was 8.8%, which was a mere 1.2% increase compared to the previous year. The cost of material and services is an essential factor that could affect the operating margin. The main reason is the increase in fuel costs was EUR 5.2 billion, of which 5.8 percentage points was due to the merger of Brussels Airlines. At the same time, it also caused an 11.3% increase in the fee, an increase in air traffic control fees and air traffic tax. Other service costs rose by 22.9%, mainly due to the charter service of the SunExpres and Air Berlin in the point-to-point aviation sector. (Investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com, 2018)
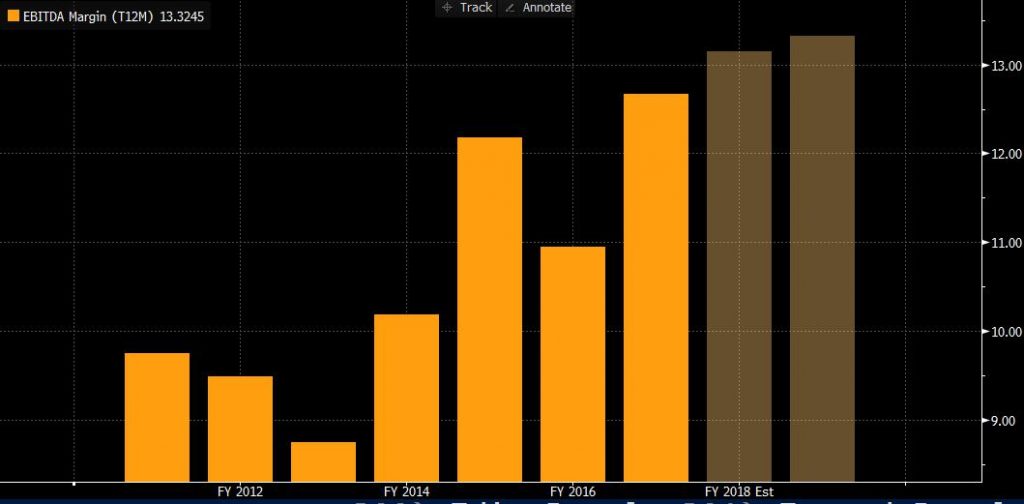
2.3. EBIT and EBITDA margin
As a result of the increase in operating activities, EBIT also increased. In 2017, the EBIT was EUR 3.310 billion, an increase of approximately 45.5% compared to 2016. The EBITDA margin is 13.3245%, which is the highest compared to the previous five years. 6.56% lower than its competitors, British Airways PLC. At the same time, ROCE also rose to 12.8%, an increase of 3.8 percentage points from 2016 and 2.76% lower than British Airways PLC. This shows that the overall efficiency of the use of available resources has increased, and Lufthansa’s basic profit has remained stable.
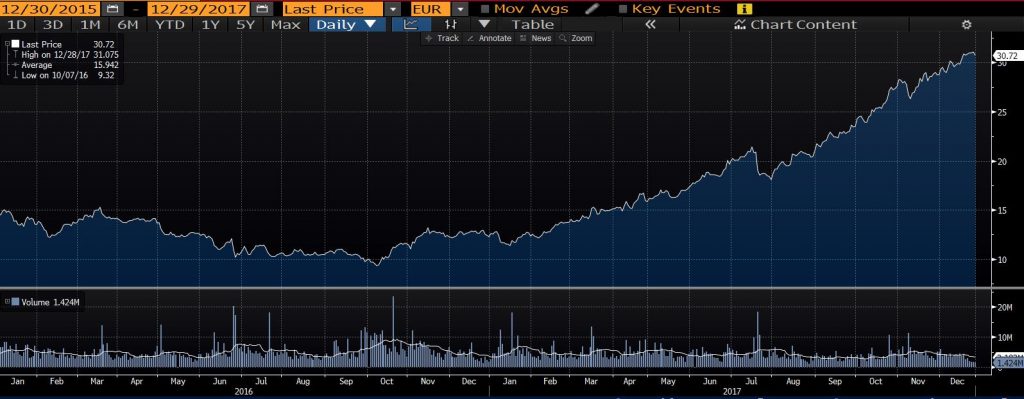
2.4. Share price
In 2017, Lufthansa’s share price rose astonishingly by 150.4%. The year-end share price is EUR 30.72. It can be seen from the line chart that there is a clear upward trend in 2017. Although there was a drop in July, it rebounded sharply in early August, and there was no significant floating decline. The reasons for the sharp increase is the enormous profits in 2017 and the perfect implementation of the strategy. In Europe, the bankruptcy of Monarch Airlines and Air Berlin has brought a large number of passengers to Lufthansa. In addition, in Asia, Lufthansa’s increasing number of joint ventures have also won a lot of market share for it. For example, on October 24, 2017, Lufthansa and China’s Alibaba Group’s Fliggy signed a strategic cooperation agreement, which substantially increased the number of passengers from Asia.
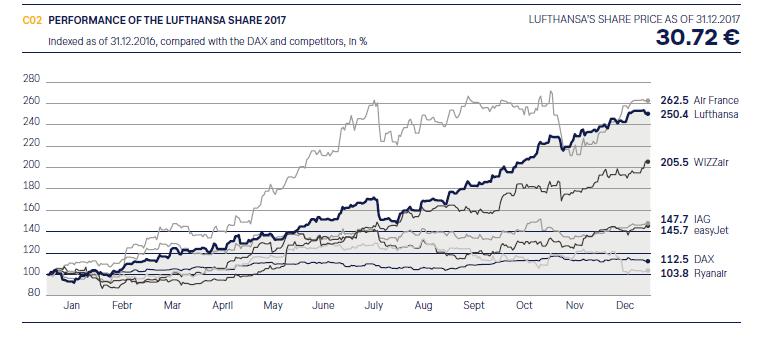
Figure 2
From the line chart above, we can see that the stock price of the aviation industry has risen in 2017 as a whole. Among them, Air France has risen sharply in May.
From the line chart above, we can see that the stock price of the aviation industry has risen in 2017 as a whole. Among them, Air France has risen sharply in May. British Airways’ share price also showed a steady upward trend at the same time. In particular, it reached the highest point on October 20, 2017, 657.5GBP.
3. Position
3.1. Goodwill and other intangible assets
In 2017, goodwill and intangible assets were EUR1.835 billion, an increase of 5.6% compared to 2016. Among them, goodwill increased by 12.1% compared to last year, and intangible assets increased by 0.19%. The reason is that the acquisition of AIR Dolomiti S.p.A will bring goodwill to distribute in the company’s department. The brand’s impairment remained almost unchanged from 2016. On November 4, 2017, Lufthansa was evaluated as a five-star by Skytrax and became the first airline to receive this honour outside of Asia.
3.2. Total liability
Total liability decreased by EUR 0.879 billion to EUR 26.669 billion compared to last year. Non-current liabilities are EUR 14billion, a decrease of EUR 2.5 billion compared to 2016, of which the pension provision in non-current liabilities is EUR 3.2 billion less than in 2016, mainly due to the EUR 1.7 billion invested in the plan for the first time in the fiscal year. Company’s cabin crew excessive welfare program. Current liability rose to EUR 12.6 billion. The reason for this result was that trade payables rose by nearly EUR 561 million.
3.3. Long-term solvency
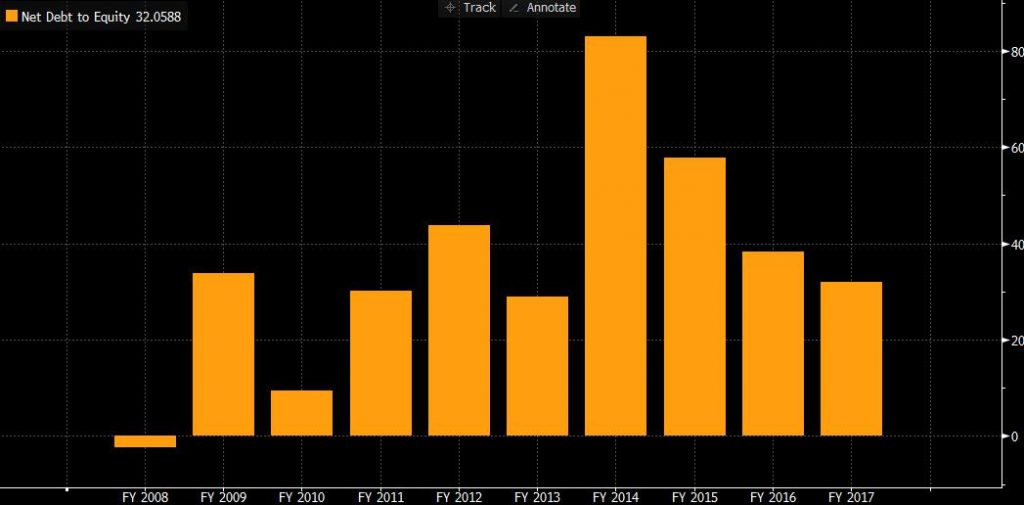
Figure 3
In 2017, the gearing was 32.059%, but for a more comprehensive analysis, the pension proposal should add to the net debt which was 83.4%, compared with 2016, there was a dramatic change from 154.8%. It means the net debt in 2017 is already less than equity. Although it both have increased in 2017, the movement of equity is very significant.
As mentioned above, the profit in 2017 rose dramatically which leading to an increase in equity. Even the gearing has declined, the gearing ratio remains relatively high, which shows Lufthansa uses debt to pay for its operations and investments. Such as the majority purchase of the Air Berlin group, which leads to higher leverage, and once the company’s profits decline, high asset-liability ratios will bring trouble to the company to repay debts.
The interest coverage in 2017 was 7.84, which was the second-ranked number in the Lufthansa decade, indicating that the interest coverage of the group was sufficient to bring in more non-current debt financing. Long-term loans may be more affordable than large-scale overdrafts. The gearing ratio of British Airways has also reduced dramatically by 88.38%, its gearing achieved 104.05% in 2017, indicating that its debt is higher than its assets.
4. Liquidity and Cash flow
4.1. Quick ratio
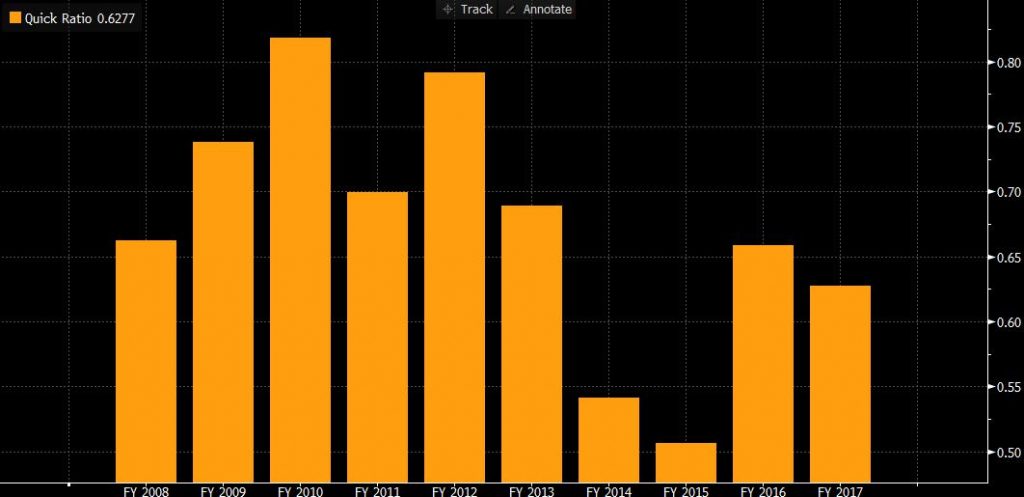
Figure 4
Compared with 2016, the current ratio decreased by 0.06 to 0.87, and the quick ratio fell by 0.05 to 0.85. Due to Lufthansa’s corporate nature, it is difficult to turn the inventories into cash efficiently, so the quick ratio can be more suitable for evaluation. In general, the reduced quick ratio represents that the company is being over-leveraged, which may be due to the increase in liabilities. For example, liabilities to banks Is EUR 20.44 billion, compared to 2016 with more than EUR 2.69 billion borrowed. In the entire industry, Lufthansa’s quick ratio leads with 62% of companies. However, because the ratio is still below than 1, this means that Lufthansa’s ability to quickly convert current assets into cash to repay debt is low. The British Airways’ quick ratio is 0.69, which shows that its ability to repay debt is lower than Lufthansa. (Fame-bvdinfo-com.liverpool.idm.oclc.org, 2018)
4.2. Receivable days
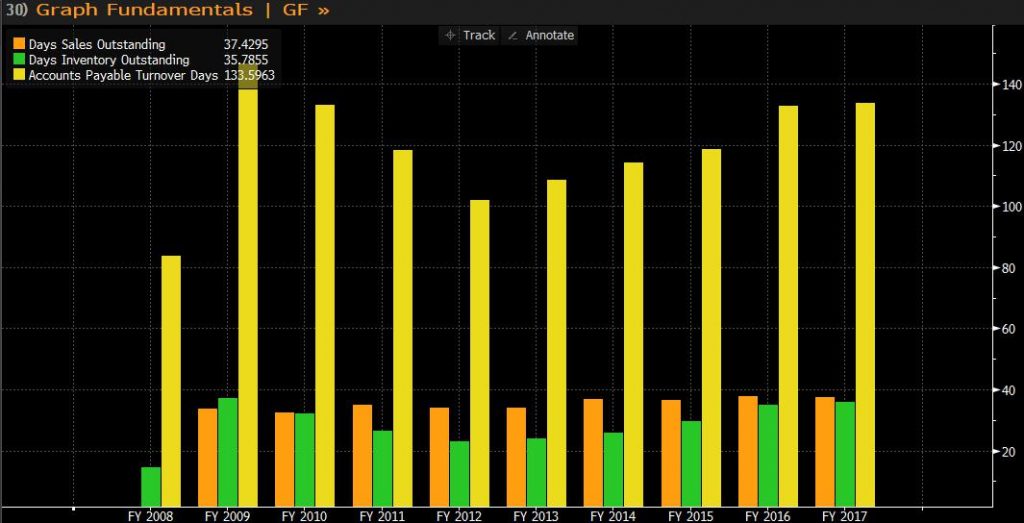
In 2017, Lufthansa’s trade receivable collection period was 37.43 days, which was a decrease of 0.24 days compared to the previous year. Even it above the average of the past decade, but Lufthansa is at a relatively low level for the entire industry. The drop in data indicates that Lufthansa’s ability to use cash has grown and it will take slightly less than the previous year to convert sales into cash,which will improve the company’s liquidity and turnover performance. (Gurufocus.com, 2018)
Trade payable days increased by 0.66 days compared with the previous year. Although the changes are relatively inconspicuous, this shows that Lufthansa has increased its cycle time when paying its suppliers. If it continues to increase, it may cause suppliers to stop supplying which would influence the fluidity significantly. Through comparison with the entire industry, Lufthansa is higher than 86% of the company.
4.3. Cash from operating activities
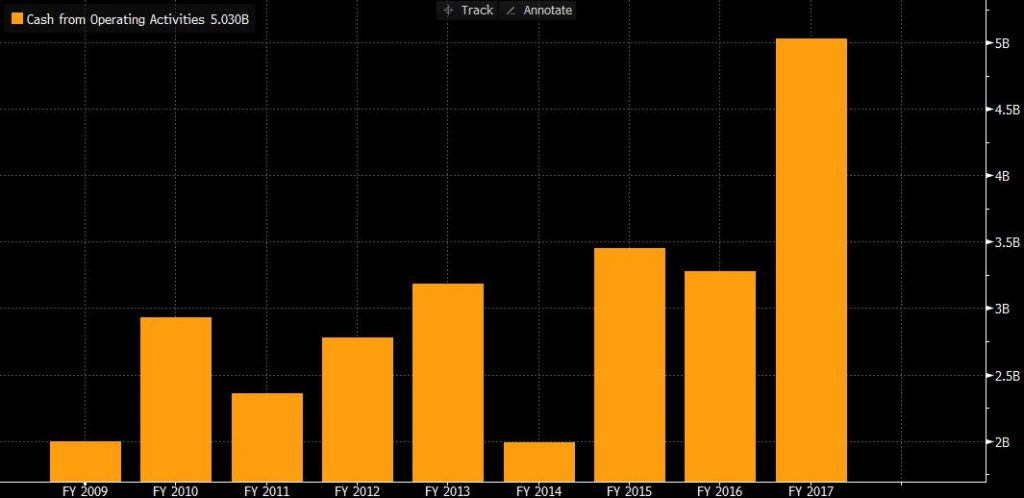
Figure 5
According to the cash flow in 2017, first of all, from the cash from operating activities, there was an increase of 55% compared to 2016. Including net profit before income tax rose by 42%. The increase mainly due to the rise of traffic revenue, which is inseparable from the acquisition. Another important reason is that the unused flight documents also caused the inflow of cash which is around EUR 423 million. (Investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com, 2018)
4.4. Cash from investment activities
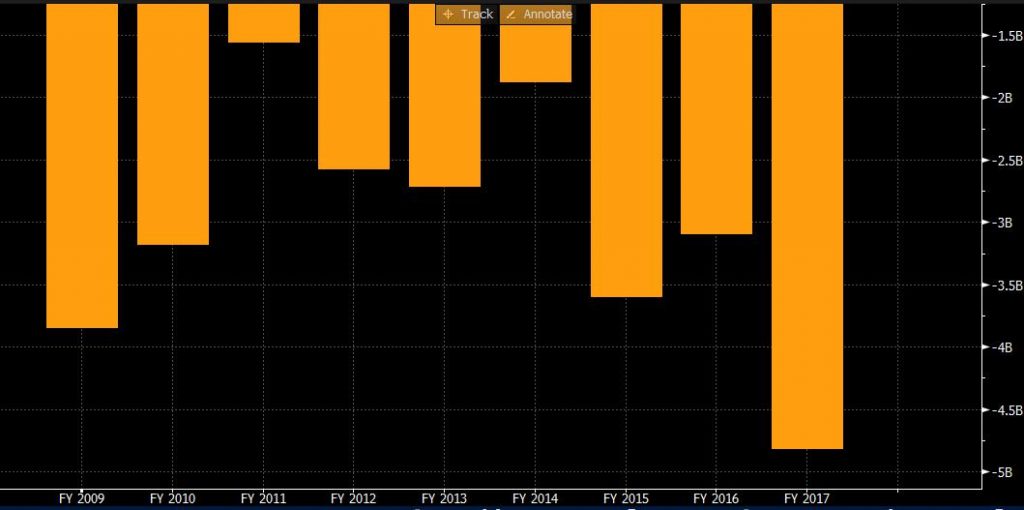
From an investment perspective, most of the investment in 2017 was more than 2016. For example, it has invested EUR 6 million for research and development for better company operations and development. Lufthansa Group stated in 2017 that it would continue to invest EUR 500 million in GDS (Global Distribution System). The reason is that the controversial GDS put forward in 2016 has already brought rewards and continues increase.
4.5. CASH ROCE
The cash return on capital employed in 2017 was 25.8%, which is an increase of 8.4% compared with the previous year. (Subscriber.hoovers.com.liverpool.idm.oclc.org, 2018) The main reason was the increase in efficiency and efficiency in 2017, which led to a rise in cash from operations. At the same time, the cash return of capital employed is higher than the ROCE of the same year, which indicates that the net assets generated excess cash profits because the Cash ROCE did not take depreciation into account. Cash quality ratio was 157% in 2017, an increase of 9 percentage points compared with the previous year. This data also proves the excess cash generated. Lufthansa can use this generated cash for financial purposes or to buy new assets. Lufthansa is 21% higher than British Airways PLC.
5. Events after balance analysis the financial performance代写
In addition, some important events occur after the Balance sheet date. These events may have an impact on performance and stock prices in 2018. First, Lufthansa acquired Luftfahrtgesellschaft on January 8, 2018All shares of Walter mbH, the purchase price of 22 million euros. Lufthansa and union ver.di signed a long-term wage agreement on 28,000 ground staff, which will require an increase of 4.9%-6.1% in the future. These salaries come from the group’s economic growth.
6. Conclusion
Based on the above analysis of the 2017 Lufthansa Group, I firmly believe that investing in the Lufthansa Group in the future can expand our investment portfolio and generate considerable returns. Although competition in the aviation industry is fierce today, threats from low-cost airlines and other competitors are growing. However, its financial stability and its response to risk companies are in the leading position in the industry. At the same time, its securities performance is excellent 7which showing a steady rise. Although there was a decline in early 2018, the profits will increase with the annual increase in corporate alliances and expansion. Therefore, investing in Lufthansa Group will have a great chance of gaining benefits.
7. Reference analysis the financial performance代写
Fame-bvdinfo-com.liverpool.idm.oclc.org. (2018). Shibboleth Authentication Request. [online] Available at: https://fame-bvdinfo-com.liverpool.idm.oclc.org/version-2018327/Report.serv?_CID=62&context=2PZIF8JGCBLLUFY&SeqNr=0 [Accessed 12 Apr. 2018].
Gurufocus.com. (2018). Deutsche Lufthansa AG Days Sales Outstanding (DLAKY). [online] Available at: https://www.gurufocus.com/term/DaysSalesOutstanding/DLAKY/Days-Sales-Outstanding/Deutsche%20Lufthansa%20AG [Accessed 12 Apr. 2018].
Investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com. (2018). [online] Available at: https://investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com/fileadmin/downloads/en/financial-reports/annual-reports/LH-AR-2017-e.pdf [Accessed 12 Apr. 2018].
Investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com. (2018). [online] Available at: https://investor-relations.lufthansagroup.com/fileadmin/downloads/en/charts-speeches/LH-APC-2018-charts-Spohr-Svensson.pdf [Accessed 12 Apr. 2018].
Subscriber.hoovers.com.liverpool.idm.oclc.org. (2018). Shibboleth Authentication Request. [online] Available at: http://subscriber.hoovers.com.liverpool.idm.oclc.org/H/company360/balanceSheets.html?companyId=41803000000000&newsCompanyDuns=315000893 [Accessed 12 Apr. 2018].
8. Appendices analysis the financial performance代写
8.1. Operating margin
8.2. EBITDA margin
8.3. Share price
8.4. Goodwill
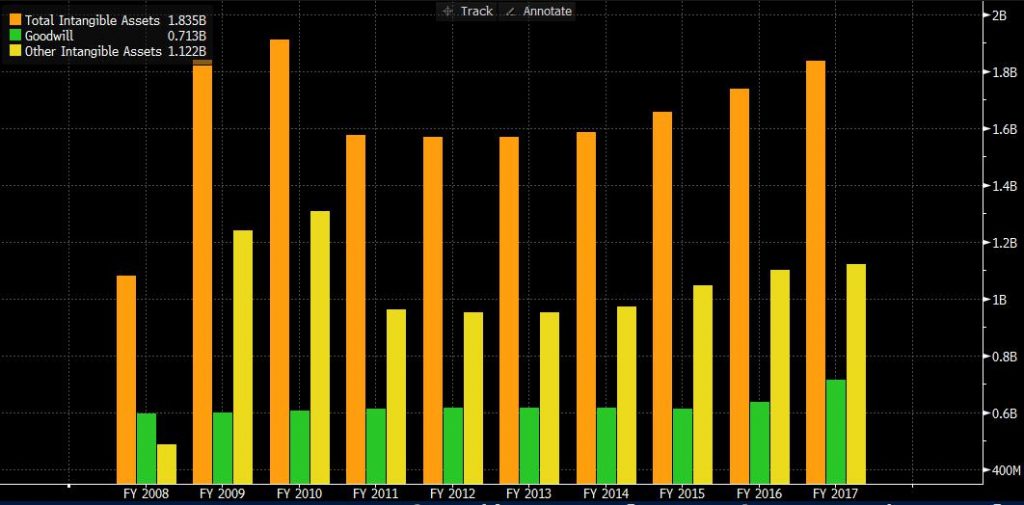
8.5. Total liabilities
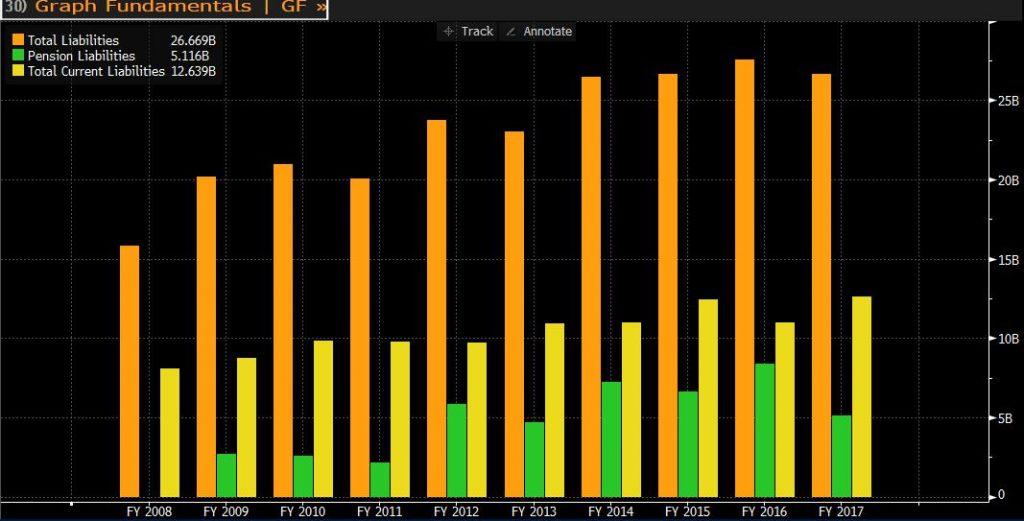
8.6. Receivable days
8.7. Cash from investment activities
更多其他:prensentation代写 网课代修 代写CS 数据分析代写 润色修改 代写案例 Assignment代写 助学金申请 成品购买




您必须登录才能发表评论。