Strategic Decision Theory
商科金融代写 A seller wishes to auction a single indivisible object among n potential buyers each of whom has values drawn independently…
Problem Set 8
1 Problem 1 – A Simple Auction 商科金融代写
A seller wishes to auction a single indivisible object among n potential buyers each of whom has values drawn independently from some absolutely continuous distribution F on [0, 1] with the associated density f . Let vi be buyer i ’s valuation. The auction mechanism used is a sealed-bid second price auction. Ties are broken by assigning the object randomly to one of the highest bidders.
Suppose the seller’s valuation is also drawn from F independently and that he also sub- mits a bid. If the seller’s bid is the highest, he simply keeps the object and his payoff is equal to his valuation. If not, the highest bidder pays the second highest bid, and the seller’s pay- off is the payment received from the winner. We thus have a sealed second-price auction with (n + 1) bidders.
(a) Confirm that it is still a weakly dominant strategy for buyers to submit their own val- uations, regardless of the seller’s valuation and bid.
(b) Letv(i) be the i -th highest valuation among n Show that 商科金融代写
Pr(x > v(1)) = F (x )n
Pr(v(2) < x < v(1)) = n (1 − F (x ))F (x )n−1
Pr(v(2) < x ) = F (x )n + n (1 − F (x ))F (x )n−1

(c) Suppose that buyers play their weakly dominant Show that the seller’s ex- pected payoff when his true valuation is v and his bid is b is given by
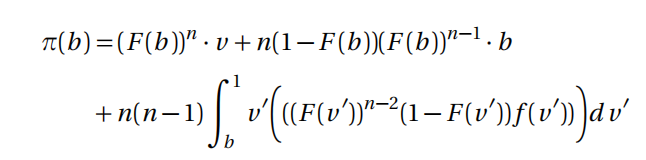
Hint: Show that 商科金融代写
- The first term corresponds to the case b > v(1)
- The second term corresponds to the case v(2) < b < v(1)
- The third term corresponds to the case v(2)> b . You will find it useful to define the distribution function of the second highest valuation conditional on v(2) > b , which is given by G (x ) = Pr(b < v(2) < x )/Pr(v(2) > b ) for x ≥ b and to compute its associated density g (x ) = G F(x ).
Note: You can answer (d )-( f ) correctly using π(b ) as given above even if you cannot fully answer (c ).
(d) Argue that it is not optimal for the seller to bid his true valuation. 商科金融代写
(e) Derive the seller’s optimal bid function when F is a uniform distribution.
(f) Suppose that the seller cannot make a bid by himself, possibly because a law or some other rule prohibits her from doing Revert to the assumption that the seller’s valu- ation is zero. Use the results you have obtained above to suggest a modification of the second price mechanism which leads to an increase in the seller’s expected payoff.




