International Economic Coordination and Governance
国际经济协调与治理
国际经济 Capitalism and democracy are some of the critical tenets of a modern global society that greatly depend on international trade. And ···
Introduction
Capitalism and democracy are some of the critical tenets of a modern global society that greatly depend on international trade. And multinational relationship to improve human living standards. Some of the anchoring principles of capitalism and democracy were developed when the world was not a global system with such a large number of interconnected units. Capitalism systems experience numerous flows that originate from the continuous expansion of the global society and the organizations around the world.
Some of these flows if not mitigated in time often culminate into a full-blown crisis that affects a large number of countries. Varoufakis and Streeck explore some of the critical elements of capitalism and democracy to establish the causes of crises and the possible remedies that could improve the situation in a global scale. With the expansion of trade across the globe and high dependence on technology, a financial crisis may lead to a collapse of critical institutions. This paper will assess Varoufakis and Streeck’s views on the impact of capitalism and democracy on the world financial systems.
译文:介绍 国际经济
资本主义和民主是高度依赖国际贸易的现代全球社会的一些关键原则。与多国关系提高人类生活水平。资本主义和民主的一些基本原则是在世界还不是一个拥有如此大量相互关联单位的全球体系时发展起来的。资本主义系统经历了许多源于全球社会和世界各地组织的不断扩张的流动。
其中一些流动如果不及时缓解,往往最终演变成影响许多国家的全面危机。 Varoufakis 和 Streeck 探讨了资本主义和民主的一些关键要素,以确定危机的原因以及可以在全球范围内改善局势的可能补救措施。随着全球贸易的扩张和对技术的高度依赖,金融危机可能会导致关键机构的崩溃。本文将评估 Varoufakis 和 Streeck 关于资本主义和民主对世界金融体系影响的观点。
Surplus Recycling Mechanism, in Varoufakis’ View
To understand the world surplus mechanism, it is essential to look at how the world surplus arises. In a two-country economy, surpluses may arise due to imbalances in capital flow between the countries. To determine the trade deficits and the trade surplus, one can use a formula that relates the exports to the imports of a particular country as follows; .
A negative balance of trade is considered a deficit while a positive balance of trade is considered a surplus. A country with a deficit has to borrow money to finance its expenditure while the countries with surplus lend money to the countries with deficits leading to significant instability due to huge surplus in a few countries.
Figure 1 Flow of Goods and Finance in International Trade
(图 1 国际贸易中的商品和资金流向)
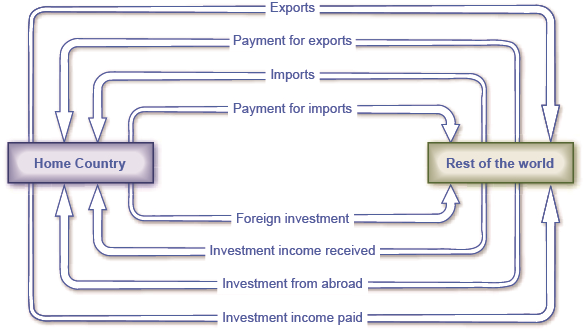
译文:Varoufakis 眼中的剩余回收机制
要理解世界盈余机制,必须先了解世界盈余是如何产生的。 在两国经济中,由于国家之间的资本流动不平衡,可能会出现盈余。 要确定贸易逆差和贸易顺差,可以使用如下公式将特定国家的出口与进口联系起来: .
负的贸易差额被认为是逆差,而正的贸易差额被认为是顺差。 有赤字的国家不得不借钱为支出提供资金,而有盈余的国家则向有赤字的国家借钱,由于少数国家的巨额盈余,导致严重的不稳定。
And
Varoufakis believes that countries with long-term trade surplus should invest in less developed countries to balance the world economy. A term called surplus recycling mechanism. Marshal plan is one of the agreements that encouraged surplus mechanism to correct some of the world financial problems after world war II (Varoufakis, 2015).
It is essential to note that the marshal plan and similar policies took place in Asia, majorly for political reasons. Varoufakis indicates no significant reason for such transfers. Countries with trade surplus also need to keep their trading partners in good shape (Varoufakis, 2015). Varoufakis’ surplus recycling mechanism originates from Keynes’s policies on the trade surplus.
Keynes realized that countries running long-term trade surplus could harm their trading partners. In global trade, the net exporters usually tend to extract money from their trading partners as most of the money is spent on their product while they spend little on imports (Kacperczyk & Schnabl, 2009). The countries with persistent surplus suck up global money. Leading to low capital in their trading partners.
Suppose the net export countries only invest the money in their domestic market. In that case, it will lead to instability in the global market as their trading partners lack the capital to invest in their domestic market (Kacperczyk & Schnabl, 2009). Lack of investment in the domestic market for net importers leads to a reduction in income and job opportunities, leading to poverty.
Varoufakis believes that a global surplus recycling mechanism can correct some of these anomalies (Varoufakis, 2015). Varoufakis also think that there is a need for an automated global surplus recycling mechanism that would keep the system in check at all times to ensure that all countries maintain a reasonable economic level.
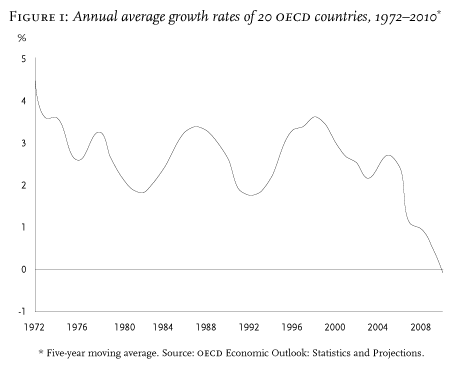
Figure 2 Long Term Causes of Crisis (Streeck, 2011)
(图 2 危机的长期原因(Streeck,2011))
译文:国际经济
瓦鲁法基斯认为,长期贸易顺差的国家应该向欠发达国家投资,以平衡世界经济。一个术语叫做盈余回收机制。元帅计划是二战后鼓励盈余机制纠正部分世界金融问题的协议之一(Varoufakis,2015)。必须指出,元帅计划和类似政策发生在亚洲,主要是出于政治原因。 Varoufakis 表示没有进行此类转移的重要原因。拥有贸易顺差的国家也需要保持其贸易伙伴的良好状态(Varoufakis,2015)。 Varoufakis 的盈余回收机制源于凯恩斯的贸易顺差政策。凯恩斯意识到,长期贸易顺差的国家可能会损害其贸易伙伴。在全球贸易中,净出口商通常倾向于从其贸易伙伴那里榨取资金,因为大部分资金都花在了他们的产品上,而他们在进口上的花费很少(Kacperczyk & Schnabl,2009)。持续盈余的国家吸纳了全球资金。导致其贸易伙伴的资本不足。假设净出口国仅将资金投资于其国内市场。在这种情况下,由于其贸易伙伴缺乏投资国内市场的资本,这将导致全球市场不稳定(Kacperczyk & Schnabl,2009)。净进口国缺乏对国内市场的投资导致收入和就业机会减少,从而导致贫困。Varoufakis 认为,全球盈余回收机制可以纠正其中一些异常现象(Varoufakis,2015 年)。 Varoufakis 还认为,需要一个自动化的全球盈余回收机制,让系统始终处于受控状态,以确保所有国家保持合理的经济水平。
To correct the imbalances brought by continued surpluses
Keynes proposed a system to monitor and update the imbalance. The organization would impose taxes on countries with surplus trade beyond a certain level (Acharya & Schnabl, 2010). The finances generated from the interest charged were to be invested in countries with long-term deficits. The interest could be managed by unions or through the global surplus recycling body.
For instance, in Eurozone, Germany, and a few other countries have a long-term trade surplus (Lawless, 2016). The European Union can impose interest on counties’ exports beyond a certain level. The amount generated from the interest charged is then invested in countries with net imports from these countries. A central organization could handle the global surplus recycling process that was to be formed if Keynes’s advice was taken into consideration.
According to Varoufakis, the global system has been anchored on United State’s benevolence capability. After World War II, the global financial system was designed with the US as the worldwide surplus nation that would use its powers to maintain a stable international monetary system (Lawless, 2016). The US has not lived to the expectation as most of the financial plans assumed that lack of self-restrain would not negatively affect the country.
译文:纠正持续盈余带来的失衡 国际经济
凯恩斯提出了一个监测和更新失衡的系统。该组织将对贸易顺差超过一定水平的国家征税(Acharya & Schnabl,2010)。利息产生的资金将投资于有长期赤字的国家。利益可以由工会或通过全球剩余回收机构管理。例如,在欧元区,德国和其他一些国家有长期贸易顺差(Lawless,2016 年)。欧盟可以对超过一定水平的国家出口征收利息。然后将利息产生的金额投资于从这些国家净进口的国家。如果考虑到凯恩斯的建议,一个中央组织可以处理将要形成的全球剩余回收过程。根据瓦鲁法基斯的说法,全球体系一直以美国的仁慈能力为基础。二战后,全球金融体系被设计为美国作为全球盈余国家,将利用其权力维持稳定的国际货币体系(Lawless,2016 年)。美国没有达到预期,因为大多数财务计划都假设缺乏自我约束不会对该国产生负面影响。
Varoufakis also believe that the US used its position in the global economic system to maintain its expenditure after world war II.
Leading to crises such as that witnessed in 2007/08 (Varoufakis, 2015). To correct the consequences of depending on a single country for global finical management, Varoufakis believes that there should be a global system to regulate the global financial system. The international system should be anchored on a surplus recycling mechanism to ensure that all the developing countries are supported.
With a strategy to ensure that all the surplus is correctly invested, Varoufakis believes that the world can reduce the impact of the global financial crisis moving forward (Lawless, 2016). Countries in the same region are generally affected by the financial crisis in a country within the region. The spread of effect happens because most of the economic policies are shared within a region.
For instance, a reduction in the Euro’s strength affects all the countries within the European Union (Lawless, 2016). To maintain a stable economy within a region, countries with a surplus should invest in countries with deficits. As stated by Varoufakis, the surplus recycling mechanism will maintain economic stability at the regional level.
译文:瓦鲁法基斯还认为,美国在二战后利用其在全球经济体系中的地位来维持其支出。国际经济
导致诸如 2007/08 年目睹的危机(Varoufakis,2015 年)。为了纠正全球金融管理依赖单一国家的后果,瓦鲁法基斯认为,应该有一个全球体系来规范全球金融体系。国际体系应以盈余回收机制为基础,以确保所有发展中国家都得到支持。通过确保所有盈余正确投资的战略,Varoufakis 相信世界可以减少全球金融危机的影响(Lawless,2016 年)。同一地区的国家普遍受到地区内某国金融危机的影响。之所以会扩散效应,是因为大部分经济政策是在一个区域内共享的。例如,欧元走强会影响欧盟内的所有国家(Lawless,2016 年)。为了保持区域内经济的稳定,顺差国家应该投资于逆差国家。正如瓦鲁法基斯所说,剩余回收机制将维持区域层面的经济稳定。
What does Varoufakis mean by the “Global Minotaur” model?国际经济
To understand the meaning of global Minotaur, it is essential to look back at the history of the word Minotaur. Minotaur comes from a create mythology that involves King Minos and Poseidon. King Minotaur requested a sacrificial bull as an endorsement of his rule. Poseidon refused to offer a bull as requested, enraging the king.
In anger, the gods had Mino’s wife fall in lust with a bull, producing a Minotaur. Other states had to pay tribute to King Mino as their supreme leader. King Aegeus of Anthe managed to slaughter the bull, freeing Athens from Cretan rule. In Varoufakis’s view, the Minotaur represents the USA. The tribute paid to the US is the capital flow from other nations around the world (Varoufakis, 2015).
Evaluation of a crisis depends on the cause of the crisis, the immediate trigger of the crisis, and the propagation of the crisis to other parts of the country and the world. The US economy in the 1980s experienced significant growth in the manufacturing and financial sectors. The growth of the manufacturing sector led to a substantial increase in export (Acharya & Schnabl, 2010).
译文:Varoufakis 所说的“全球牛头怪”模型是什么意思? 国际经济
要理解全球牛头怪的含义,有必要回顾一下牛头怪这个词的历史。牛头怪来自一个涉及国王米诺斯和波塞冬的创造神话。牛头怪国王要求一头献祭的公牛作为对他统治的认可。波塞冬拒绝按要求提供公牛,激怒了国王。一怒之下,众神让米诺的妻子对一头公牛产生了欲望,产生了牛头怪。其他国家不得不向米诺国王致敬,作为他们的最高领袖。 Anthe 的 Aegeus 国王设法杀死了公牛,将雅典从克里特岛的统治中解放出来。在瓦鲁法基斯看来,牛头怪代表美国。向美国致敬的是来自世界其他国家的资本流动(Varoufakis,2015 年)。对危机的评估取决于危机的原因、危机的直接触发因素以及危机向国家和世界其他地区的传播。 1980 年代的美国经济在制造业和金融部门经历了显着增长。制造业的增长导致出口大幅增加(Acharya & Schnabl,2010 年)。
Despite growth in manufacturing and industrialization
Wages remained constant in most parts of the 20th century (Varoufakis, 2015). Many companies had surplus income from profits generated in different countries. Since most of the USA’s capital came from other countries, more so developing countries were majorly consumers but not manufacturers. Furthermore, due to low wages, most workers started borrowing money to purchase houses and sustain their lifestyle. Due to poor financial policies, the US borrowed most of the deficit from the international market.
Most of the developing countries had a capital shortage as their borrowing power was low (Varoufakis, 2015). May investors would prefer to lend money to a prosperous country instead of lending to unstable countries. A massive influx of capital was borrowed by US citizens under weak financial policies. The influx of money and advancement of export made the US stable as other countries suffered until the great financial crisis of 2007/08 happened.
Furthermore 国际经济
Varoufakis explores the impact of the Bretton woods agreement on the US economy before the financial crisis. One of the agreement’s significant defects was the lack of a surplus recycling mechanism in the Marshal plan that allowed the US to invest its surplus dollars in Japan and Germany. After the collapse of the gold exchange, US had a deficit in financing some of its wars in Vietnam and South East Asia.
Varoufakis indicate that the US persuaded OPEC to raise the oil price as the US dollars majorly dominated it. A rise in the oil prices would lead to a demand in the US dollars (Streeck & Yamamura, 2018). The world continued to fund the US deficit as the US dollars were still regarded as one of the major reserve currencies.
Thus, the US economy was expanding with cheap wages leading to increased profitability which further led to capital inflow from other parts of the world (Adrian & Shin, 2010). Despite crises in other parts of the world, the US remained stable as most of the capital was directed to the country. Other countries suffered because the increase in US dollar price reduced their purchasing power, more so for oil that was a significant factor of production.
译文:尽管制造业和工业化增长 国际经济
在 20 世纪的大部分时间里,工资保持不变(Varoufakis,2015)。许多公司从不同国家产生的利润中获得了盈余收入。由于美国的大部分资本来自其他国家,因此发展中国家主要是消费者而非制造商。此外,由于工资低,大多数工人开始借钱买房和维持生活。由于财政政策不力,美国从国际市场借走了大部分赤字。
大多数发展中国家由于借贷能力低而存在资本短缺(Varoufakis,2015 年)。可能投资者更愿意把钱借给一个繁荣的国家,而不是借给不稳定的国家。在疲软的金融政策下,美国公民借入了大量资本。资金的流入和出口的增加使美国在其他国家遭受苦难的情况下保持稳定,直到2007/08年的大金融危机发生。此外,Varoufakis 探讨了布雷顿森林协定对金融危机前美国经济的影响。该协议的重大缺陷之一是元帅计划中缺乏盈余回收机制,允许美国将其盈余美元投资于日本和德国。黄金交易所倒闭后,美国在越南和东南亚的一些战争中出现了资金赤字。
Varoufakis 表示,美国说服欧佩克提高油价,因为美元主要占主导地位。油价上涨将导致对美元的需求(Streeck & Yamamura,2018 年)。由于美元仍被视为主要储备货币之一,世界继续为美国赤字提供资金。因此,美国经济以低廉的工资扩张,从而提高了盈利能力,进而导致资本从世界其他地区流入(Adrian & Shin,2010 年)。尽管世界其他地区出现危机,但美国仍保持稳定,因为大部分资金都流向了该国。其他国家由于美元价格上涨降低了他们的购买力而受到影响,对于作为重要生产要素的石油而言更是如此。
Wolfgang Streeck argues that the advanced capitalist economies have been in crisis (‘buying time’) since the 1980s
Wolfgang Streeck is one of the most critical voices on the crisis of global capitalism and its impact on democracy and governance worldwide. It’s essential to understand his view on the crisis of advanced capitalists worldwide to peer into capitalism’s effects. Early on, Wolfgang Streeck believed that capitalism. And democracy could be merged under the proper institutional supervision to bring out the best parts of the two systems while suppressing their negative differences (Streeck, 2011).
As time passed, Wolfgang Streeck became more concerned by the compatibility between distributive politics, redistributive politics, and capitalism in a global economy. The analysis drove Wolfgang Streeck to see a significant incompatibility between democracy and capitalism (Streeck & Yamamura, 2018). Wolfgang Streeck strongly believes that capitalism is in critical condition compared to any other time after world wars.
The global crisis since 1980 has affected different elements of society, more so the financial systems. Many economists believe that the crises are merely a disturbance or deviation from the norm of a much complex and organized system. Furthermore, world systems are generally viewed as self-correcting and tending towards equilibrium at all times (Adrian & Shin, 2010).
译文:Wolfgang Streeck 认为,自 1980 年代以来,发达资本主义经济体一直处于危机之中(“购买时间”)国际经济
Wolfgang Streeck 是全球资本主义危机及其对全球民主和治理的影响的最重要的声音之一。了解他对全球先进资本家危机的看法对于观察资本主义的影响至关重要。早期,沃尔夫冈·斯特里克相信资本主义。民主可以在适当的制度监督下合并,以发挥两个系统的最佳部分,同时抑制它们的负面差异(Streeck,2011)。随着时间的推移,Wolfgang Streeck 越来越关注全球经济中分配政治、再分配政治和资本主义之间的兼容性。分析促使 Wolfgang Streeck 发现民主与资本主义之间存在严重的不相容性(Streeck 和 Yamamura,2018 年)。 Wolfgang Streeck 坚信,与世界大战后的任何时期相比,资本主义都处于危急状态。自 1980 年以来的全球危机影响了社会的不同元素,金融系统更是如此。许多经济学家认为,危机仅仅是对一个非常复杂和有组织的系统规范的干扰或偏离。此外,世界体系通常被视为自我修正并始终趋于平衡(Adrian & Shin,2010)。
Wolfgang Streeck believes that 国际经济
The crises are a deviation from the norm and part of the underlying systems supporting global capitalism (Streeck, 2011). The crises then become the rule rather than the exception as the tension remains a regular part of the system leading to instability and disequilibrium. Streeck indicates that the crisis symptoms are numerous, but the major ones include persistent economic growth rate decline.
Furthermore, an increased indebtedness of major capitalists also aggravates the situation. Economic inequality in wealth and income also forms a major part of the catalyst (Adrian & Shin, 2010). Streeck argues that these major catalysts of crises have been on the rise for a long time and continue to rise over the years in most of the major capitalists (Streeck, 2011). There is a constant crisis brewing in the capitalist systems, making these countries very unstable in the long run.
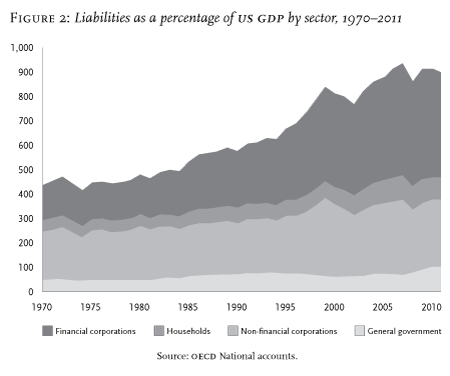
Figure 3 Debt Distress (Streeck, 2011)
Streeck further states that there is a rise of consolidations states which leads to displacement of the classic tax state by a debt state. The process is common in wealthy capitalists since the 1980s as a response to the fiscal crisis of the state after the end of post wars growth (Acharya & Schnabl, 2010). Long-time growth in debts and attempts to control the growth has led to the funding of advanced capitalisms and its mechanisms.
In Streeck’s view, such activities only make the situation worse as most of the underlying problems attached to debt are not addressed (Streeck, 2011). Further increases in debt will likely lead to more crises. Streeck also indicates that most of the countries’ debts coupled with non-Keynesian deficits in public debts will lead to the capitalist system’s collapse. Most of the current fiscal activities only buy time before the crisis comes knocking on everyone’s door.
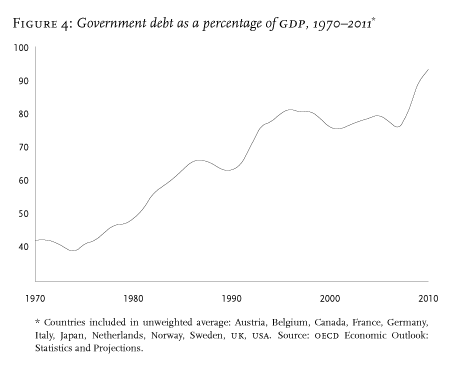
Figure 4 Rise of Government Debts (Streeck, 2011)
(图 4 政府债务的增加(斯特雷克,2011 年))
译文:Wolfgang Streeck 认为 国际经济
危机是对规范的偏离,也是支持全球资本主义的底层系统的一部分(Streeck,2011)。然后,危机成为规则而不是例外,因为紧张局势仍然是导致不稳定和不平衡的系统的常规部分。斯特里克表示,危机征兆有很多,但主要是经济增长率持续下降。此外,主要资本家的债务增加也加剧了这种情况。财富和收入方面的经济不平等也是催化剂的主要部分(Adrian & Shin,2010 年)。 Streeck 认为,这些主要的危机催化剂长期以来一直在上升,并且在大多数主要资本家中持续上升(Streeck,2011)。资本主义制度中不断酝酿着危机,从长远来看,这些国家非常不稳定。
斯特里克进一步指出,合并国家的兴起导致传统税收国家被债务国家取代。自 1980 年代以来,作为对战后增长结束后国家财政危机的回应,这一过程在富有的资本家中很常见(Acharya & Schnabl,2010)。债务的长期增长和控制增长的尝试导致了对先进资本主义及其机制的资助。在 Streeck 看来,此类活动只会使情况变得更糟,因为与债务相关的大多数潜在问题都没有得到解决(Streeck,2011 年)。债务的进一步增加可能会导致更多的危机。斯特里克还指出,大多数国家的债务加上非凯恩斯主义的公共债务赤字将导致资本主义体系的崩溃。当前的大多数财政活动只是在危机敲响每个人的大门之前争取时间。
Why does Varoufakis think the Global Minotaur has been disabled, maybe badly, by the 2007-08 crisis? 国际经济
Varoufakis indicate that the 2007-08 financial crisis led to a significant change in the US financial system. Previously, the US managed to have surplus which it invested in Germany and Japan to recycle the surplus. During the wars in East Asia, the US created a significant deficit in its economy. Furthermore, after leaving the gold standards, the US economy was majorly supported by Germany and Japan’s surpluses.
After world war II, the US economy experienced rapid growth coupled with stagnant wages (Streeck & Yamamura, 2018). Due to the deregulation of financial institutions, the US maintained a significant domestic consumption. Furthermore, the expanding European and Asian economies provided a substantial market for US goods.
After the crisis, the US economy contracted significantly, affecting Japan, Germany, and China (Streeck & Yamamura, 2018). Consequently, there was a significant skepticism in US investment in the affected countries. Due to unreliability of the US backed currencies many countries would not trust the US as a single trading partner and major investment destination after the crisis. Reduction in investment and market makes it impossible for the US to enjoy its previous position as the global Minotaur.
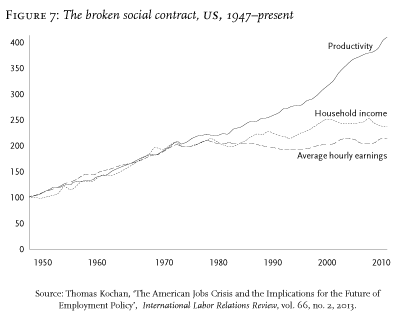
Figure 5 Broken social contracts (Streeck, 2011)
(图 5 破碎的社会契约(Streeck,2011)
译文:为什么 Varoufakis 认为全球牛头怪在 2007-08 年的危机中已被禁用,甚至可能很严重? 国际经济
Varoufakis 表示,2007-08 年的金融危机导致美国金融体系发生重大变化。此前,美国设法有盈余,它投资于德国和日本以回收盈余。在东亚战争期间,美国在其经济中造成了巨大的赤字。此外,退出金本位制后,美国经济主要靠德国和日本的盈余支撑。二战后,美国经济快速增长,工资却停滞不前(Streeck & Yamamura,2018 年)。由于金融机构放松管制,美国保持了大量的国内消费。此外,不断扩张的欧洲和亚洲经济体为美国商品提供了一个巨大的市场。危机后,美国经济大幅收缩,影响到日本、德国和中国(Streeck & Yamamura,2018 年)。因此,人们对美国在受影响国家的投资持严重怀疑态度。由于美国支持的货币不可靠,许多国家不会相信美国是危机后的单一贸易伙伴和主要投资目的地。投资和市场的减少使美国无法享有其先前作为全球牛头怪的地位。
Streeck believed that there had been a growing conflict between capitalism.
And democracy that has led to financial crisis and sovereign debt crisis. Many nations managed to marge democracy with capitalism to maintain a level play ground in the global economic system. As indicated by Streeck, the impact of the merger has only led to disaster. One of the classic disasters is the 2007-08 financial crisis that mainly originated from lack of financial supervision.
Streeck believes that the financial crisis of 2007-08 the end of the buying time. And many people could now see the impact of unregulated capitalism. Many countries and IMF started regulating their financial systems to avoid a repeat of the financial crisis (Acharya, Afonso, & Kovner, 2017). One of the major changes in the global economic system was reducing US investments by major nations such as Japan and Germany.
Furthermore, the US government decided to nationalize many companies to maintain equilibrium. Streeck believes that capitalism’s death began with the crisis as many countries were convinced of its impact because the nationalization is not common in pure capitalistic countries (Streeck, 2011). Furthermore, democracy has had a significant impact on capitalism’s progress over the years before the crisis.
After the crisis, it was clear that political policies affecting the market equilibrium should be scrutinized to reduce the unintended effect. Countries must have stringent financial systems to manage the impact of democracy on capitalism. Streeck is right to assume that the financial crisis of 2007-08 was the end or start of the end of democratic capitalism.
译文:斯特里克认为资本主义之间的冲突越来越大。国际经济
民主导致金融危机和主权债务危机。许多国家设法将民主与资本主义结合起来,以在全球经济体系中保持公平的竞争环境。正如 Streeck 所指出的,合并的影响只会导致灾难。典型的灾难之一是2007-08年的金融危机,主要源于金融监管的缺失。斯特里克认为,2007-08 年金融危机结束了买入时机。许多人现在可以看到不受监管的资本主义的影响。许多国家和国际货币基金组织开始对其金融体系进行监管,以避免金融危机重演(Acharya、Afonso 和 Kovner,2017 年)。全球经济体系的重大变化之一是减少日本和德国等主要国家对美国的投资。
此外,美国政府决定将许多公司国有化以维持平衡。 Streeck 认为资本主义的消亡始于危机,因为许多国家相信其影响,因为国有化在纯粹的资本主义国家并不常见(Streeck,2011)。此外,在危机前的几年里,民主对资本主义的进步产生了重大影响。危机之后,显然应该仔细审查影响市场均衡的政治政策,以减少意外影响。国家必须有严格的金融体系来管理民主对资本主义的影响。斯特里克正确地假设 2007-08 年的金融危机是民主资本主义终结的结束或开始。
Are Varoufakis’ and Streeck’s arguments about the sources of instability in global capitalism complementary or contradictory?
Global capitalism is riddled with lots of instabilities that significantly affect different elements of society. Sometimes the instability leads to crises that adversely affect the global financial systems. Furthermore, a crisis in one country often leads to economic effects on other countries connected to the affected country through trade or politically (Acharya, Afonso, & Kovner, 2017).
It is essential to look at the cause of the instabilities in the global financial system that leads to a regular financial crisis. Both Varoufakis and Streeck have varied views on global capitalism and its effect on the global financial system. While Varoufakis believes that lack of regulation is one of the critical causes of the financial crisis, Streeck believes that increased regulations and control by democratic systems are critical causes of the financial crisis. The two views are contradictory in their approach to capitalism and its effects.
According to Varoufakis, capitalism has led to a global crisis because some countries are greedy and would like to keep all the funds for themselves while leaving some countries suffering. The concentration of capital on one country led to debt distress. Some of the countries with trade deficits had to borrow to survive. Countries such as Greece experienced an economic crisis as Germany prospered in the unregulated capitalistic system (Simitis, 2016).
Varoufakis believes that
A global system should be established with the sole mandate of maintaining equilibrium through redistribution of the trade surplus to the countries with a deficit. To manage the capitalistic system, countries must think of the market and not leave it for the democratic system to correct the imbalance. Surplus recycling mechanism will ensure that all countries maintain an essential quality of life and economic growth due to capital balance. Varoufakis believes that the capital balance will shield the global financial system from crises.
According to Streeck, economic crises arise from interference by a democratic system. In democratic systems, the countries or individual benefit comes before the communal benefits. Some countries try to gain from systems that should benefit all countries instead of benefitting an individual or a particular country (Simitis, 2016). Streeck indicates that politicians try to please the voters by promising equal employment. To achieve the promise, some of the fundamental elements holding capitalism are affected, leading to a crisis.
译文:Varoufakis 和 Streeck 关于全球资本主义不稳定根源的论点是互补还是矛盾? 国际经济
全球资本主义充斥着许多不稳定性,对社会的不同元素产生重大影响。有时,不稳定会导致危机,对全球金融体系产生不利影响。此外,一个国家的危机通常会通过贸易或政治对与受影响国家相关的其他国家产生经济影响(Acharya、Afonso 和 Kovner,2017 年)。必须研究导致定期金融危机的全球金融体系不稳定的原因。 Varoufakis 和 Streeck 对全球资本主义及其对全球金融体系的影响都有不同的看法。虽然 Varoufakis 认为缺乏监管是金融危机的关键原因之一,但 Streeck 认为,民主制度加强监管和控制是金融危机的关键原因。这两种观点在对待资本主义及其影响的方法上是矛盾的。根据瓦鲁法基斯的说法,资本主义导致了全球危机,因为一些国家贪婪,希望将所有资金留给自己,而让一些国家受苦。资本集中在一国导致债务危机。一些有贸易逆差的国家不得不借贷才能生存。随着德国在不受监管的资本主义体系中繁荣昌盛,希腊等国家经历了经济危机(Simitis,2016 年)。
瓦鲁法基斯认为应该建立一个全球体系,其唯一任务是通过将贸易顺差重新分配给有逆差的国家来维持平衡。为了管理资本主义制度,各国必须考虑市场,而不是让民主制度来纠正不平衡。盈余回收机制将确保所有国家因资本平衡而保持基本的生活质量和经济增长。 Varoufakis 认为,资本平衡将保护全球金融体系免受危机的影响。斯特里克认为,经济危机源于民主制度的干预。在民主制度下,国家或个人利益先于公共利益。一些国家试图从应该使所有国家受益而不是使个人或特定国家受益的系统中受益(Simitis,2016 年)。 Streeck 指出,政客们试图通过承诺平等就业来取悦选民。为了实现这一承诺,资本主义的一些基本要素受到了影响,从而导致了危机。
For instance
the 2007-08 crisis was majorly caused by reckless borrowing and a plunge in housing prices. In the spirit of democracy, the government had relaxed its regulations on financial systems due to political actions (Streeck & Yamamura, 2018). Banks strived to give unsecured loans to customers without considering the market forces (Acharya, Afonso, & Kovner, 2017). The market forces acted on excesses and corrected the market, leading to a financial crisis. Streeck believes that the capitalist system, if left to run on its own rules without political interferences, crises can be avoided.
The two approaches have a significant difference and some similarities that make them a significant input in the debate for and against global capitalism. Varoufakis believes that reducing freedom and increase in regulation would reduce a crisis’s chances. Streeck categorically indicates that democratic capitalism is on its deathbed due to its inability to reduce interference (Streeck & Yamamura, 2018). Streeck and Varoufakis agree that capitalism is riddled with a loss of instabilities that must be corrected if the system is to stand for more years to come.
Conclusion
Capitalism and democracy have had a significant impact on society and world financial systems. Sometimes the world’s financial systems crumble under the weight of capitalism and democracy. Varoufakis believes that there should be a surplus recycling mechanism to keep capitalism in check.
In contrast, Streeck believes that capitalism cannot survive in its current state because of interference from democratic processes. Streeck’s view seems to be centered on the countries approach to capitalism. In contrast, Varoufakis’ view seems to be more of an external look. Though the base ideas are opposite, the general picture remains similar.
译文:例如 国际经济
2007-08 年的危机主要是由不计后果的借贷和房价暴跌造成的。本着民主精神,政府因政治行动而放松了对金融体系的监管(Streeck & Yamamura,2018 年)。银行努力在不考虑市场力量的情况下向客户提供无抵押贷款(Acharya、Afonso 和 Kovner,2017 年)。市场力量对过度行为采取行动并纠正市场,导致金融危机。斯特里克认为,如果让资本主义制度在没有政治干预的情况下按照自己的规则运行,危机是可以避免的。这两种方法具有显着差异和一些相似之处,使它们成为支持和反对全球资本主义的辩论的重要投入。 Varoufakis 认为,减少自由和加强监管将减少危机发生的机会。 Streeck 明确指出,民主资本主义由于无法减少干扰而濒临死亡(Streeck & Yamamura,2018 年)。 Streeck 和 Varoufakis 一致认为,资本主义充斥着不稳定性的丧失,如果该体系要在未来持续多年,就必须纠正这些不稳定性。
结论 国际经济
资本主义和民主对社会和世界金融体系产生了重大影响。有时,世界金融体系会在资本主义和民主的重压下崩溃。 Varoufakis 认为应该有一个剩余的回收机制来控制资本主义。相比之下,斯特里克认为,由于民主进程的干扰,资本主义无法在当前状态下生存。斯特里克的观点似乎集中在各国对待资本主义的方式上。相比之下,瓦鲁法基斯的观点似乎更像是一种外在的看法。尽管基本思想相反,但总体情况仍然相似。
References
Chohan, U. W. (2017). What is One Belt One Road? A surplus recycling mechanism approach. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.2997650
Simitis, C. (2016). Trajectory of the Greek financial crisis. The European debt crisis. https://doi.org/10.7765/9781526112019.00045
Streeck, W. (2011). The crisis in context: Democratic capitalism and its contradictions. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1950558
Streeck, W., & Yamamura, K. (2018). Introduction: Convergence or diversity? Stability and change in German and Japanese capitalism. The End of Diversity? 1-50. https://doi.org/10.7591/9781501711442-004
And 国际经济
Varoufakis, Y. (2015). The Global Minotaur: America, Europe and the future of the global economy. Zed Books.
Acharya, V., & Schnabl, P. (2010). Do global banks spread global imbalances? The case of asset-backed commercial paper during the financial crisis of 2007-09. https://doi.org/10.3386/w16079
Acharya, V. V., Afonso, G., & Kovner, A. (2017). How do global banks scramble for liquidity? Evidence from the asset-backed commercial paper freeze of 2007. Journal of Financial Intermediation, 30, 1-34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfi.2016.02.002
Adrian, T., & Shin, H. S. (2010). The changing nature of financial intermediation and the financial crisis of 2007-09. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.1576590
Kacperczyk, M., & Schnabl, P. (2009). When safe proved risky: Commercial paper during the financial crisis of 2007-2009. https://doi.org/10.3386/w15538
Lawless, A. (2016, January 29). The global Minotaur – Yanis Varoufakis in interview. Three Monkeys Online Magazine. https://www.threemonkeysonline.com/the-global-minotaur-yanis-varoufakis/
McGoey, L. (2017, May 25). SYRIZA’s finance minister has a big idea – but will Germany accept it? | Linsey McGoey. the Guardian. https://www.theguardian.com/commentisfree/2015/jan/30/syriza-finance-minister-big-idea-will-germany-accept-it
更多其他:经济学代考_经济学作业代写 环境学代写 数学代写 生物学代写 统计代写 商科代写




