Biodiversity and Human Welfare
Honors Biological Seminar
Biological Seminar代写 The term biodiversity refers to all life forms on earth, consisting of genetic varieties and different ecosystems.
ABSTRACT Biological Seminar代写
The term biodiversity refers to all life forms on earth, consisting of genetic varieties and different ecosystems. Either biodiversity comprises an ecological, cultural, and evolutionary process that sustains life. It involves diversity across various sources, including marine, aquatic, and terrestrial ecosystems. It forms the foundation of the vast array of ecosystem services that significantly influence human well-being.
Human beings’ decisions regarding biodiversity greatly dictate the well-being of their own life and other living things within that specific ecosystem. Therefore, it is essential to have ethical practices in our environment to have ensured our living welfare since human activities on this biota have a tremendous impact on their welfare.
INTRODUCTION Biological Seminar代写
Modern society enjoys various medications from plants improving their healthy living and consequently contributing to their well-being. Most plants produce compounds that are used in pharmaceuticals to extract valuable drugs. Plant medication knowledge has lasted over centuries, and their various uses are compiled in herbals books identifying each plant with their specific use.
Examples of beneficial plant compounds derived from plants for medication include atropine, codeine, aspirin, and dioxin. From recent research, some animals have essential chemical compounds that are used for human medicines. The FDA has approved more than five drugs based on animal compounds to treat diseases like diabetes, chronic pain, and hypertension. Biological Seminar代写
It is estimated that about 35 percent of new drugs introduced in the pharmaceuticals since 1981 are from natural compounds. Pharmaceutical companies still conduct research to find new compounds synthesized by living organisms used as medicine. These compounds from plants and animals give insight into how biodiversity sustains human existence by providing a healthy living through medication.
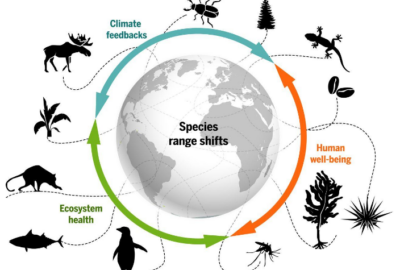
BIODIVERSITY AND AGRICULTURE Biological Seminar代写
Since the beginning of agriculture, humans have selected crop varieties and breeds to meet their food needs for more than ten years. There was high crop diversification which led to cultural diversities. For instance, potatoes were grown in the central Andes of Peru and Bolivia. The topography demands drove crop diversity, the need for crop rotation, limited human movements, and inadequate breed variety to thrive in changing climatic conditions.
However, the contemporary human population has developed crop breeds resistant to diseases that are a remarkable achievement in maintaining crop biodiversity. Seed companies worldwide should intensify their research to breed new varieties to counter the evolving pests and changes in the environment to guarantee food safety. The ability to create new resistant crops relies on the diversity of the available wild forms. Therefore, it is evident how biodiversity contributes to food security to sustain human life.
CONCLUSION Biological Seminar代写
It has been argued and established that human beings benefit psychologically from the interactions of the biodiversity world. Interactions with other living organisms greatly influence our psychological comfort. Entomologist E.O Wilson argued that human evolutionary history made humans adapt to their environment , And generated stressors that affect human health and well-being.
Also, there is evidence of psychological regenerative benefits of the landscape to human beings that suggests a human use from their environment due to these environmental diversities. Moreover, there has been an argument that humans have a moral responsibility to conserve other species since their interactions within the ecosystem improve our well-being in various ways, as discussed above.
Cited references Biological Seminar代写
- Hammen, V.C., and J. Settele. “Biodiversity and the Loss of Biodiversity Affecting Human Health.” Encyclopedia of Environmental Health, 2019, 340-350. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-409548-9.11585-4.
- Jonathan, Marks. “Health and Human Populations.” Human Biodiversity, 2017, 203-218. doi:10.4324/9780203789605-11.
- Lloyd, Pauline. “Sustainable agriculture for biodiversity, biodiversity for sustainable agriculture.” Biodiversity18, no. 2-3 (2017), 124-125. doi:10.1080/14888386.2017.1366873.
- McShane, KATIE. “WHY ANIMAL WELFARE IS NOT BIODIVERSITY, ECOSYSTEM SERVICES.OR HUMAN WELFARE: TOWARD A MORE COMPLETE ASSESSMENT OF CLIMATE IMPACTS.” Les ateliers de l’éthique13, no. 1 (2018), 43. doi:10.7202/1055117ar.
- Stinner, Deborah. “Biodiversity: Agriculture.” Terrestrial Ecosystems and Biodiversity, 2020, 17-21. doi:10.1201/9780429445651-3.
- Zhang, Zhenguo, and Jun Zhou. “From ecosystems to human welfare: the role and conservation of biodiversity.” Ciência Rural49, no. 5 (2019). doi:10.1590/0103-8478cr20170875.

生物多样性与人类福祉
荣誉生物研讨会
生物研讨会代写生物多样性一词是指地球上所有的生命形式,包括遗传变体和不同的生态系统。
摘要生物研讨会代写
生物多样性一词是指地球上所有的生命形式,包括遗传多样性和不同的生态系统。生物多样性都包含维持生命的生态,文化和进化过程。它涉及跨各种来源的多样性,包括海洋,水生和陆地生态系统。它构成了极大影响人类福祉的各种生态系统服务的基础。
人类对生物多样性的决定在很大程度上决定了该特定生态系统中自己的生活和其他生物的福祉。因此,至关重要的是在我们的环境中采取道德规范来确保我们的生活福祉,因为人类在该生物群上的活动对其福祉产生了巨大影响。
简介生物研讨会代写
现代社会享受植物提供的各种药物,改善了他们的健康生活,从而为他们的福祉做出了贡献。大多数植物产生的化合物可用于药物中提取有价值的药物。植物药物知识已经持续了多个世纪,草药的书籍中汇编了它们的各种用途,从而确定了每种植物的具体用途。
衍生自用于药物的植物的有益植物化合物的实例包括阿托品,可待因,阿司匹林和二恶英。根据最近的研究,一些动物具有用于人类药物的必需化学化合物。 FDA已经批准了五种以上基于动物化合物的药物,用于治疗糖尿病,慢性疼痛和高血压等疾病。生物研讨会代写
据估计,自1981年以来,药物中引入的新药中约有35%来自天然化合物。制药公司仍在进行研究,以寻找由用作药物的活生物体合成的新化合物。来自动植物的这些化合物通过药物提供健康的生活,从而使人们深入了解了生物多样性如何维持人类的生存。
生物研讨会代写
生物多样性与农业生物学研讨会代写
自农业开始以来,人类已经选择了多种农作物品种和品种来满足其粮食需求超过十年。高度的农作物多样化导致了文化多样性。例如,土豆在秘鲁和玻利维亚的中部安第斯山脉种植。地形条件的需求驱使作物多样性,对作物轮作的需求,有限的人类活动以及品种不足以在气候条件变化的情况下壮成长。
但是,当代人口已经开发出了对疾病具有抵抗力的作物品种,这在维持作物生物多样性方面取得了令人瞩目的成就。世界各地的种子公司应加强研究,以育种新品种,以应对不断发展的害虫和环境变化,以确保食品安全。产生新的抗性作物的能力取决于可用野生形式的多样性。因此,显而易见的是,生物多样性如何有助于维持人类生命的粮食安全。
结论生物研讨会代写
已经论证并确定,人类从生物多样性世界的相互作用中受益于心理。与其他生物的相互作用极大地影响了我们的心理舒适度。昆虫学家E.O威尔逊(E.O Wilson)认为,人类进化史使人类适应了环境,并产生了影响人类健康和福祉的压力源。
而且,有证据表明,景观对人类的心理再生益处表明由于这些环境多样性,人类从其环境中使用。此外,有一种论点认为,人类负有保护其他物种的道义责任,因为他们在生态系统中的相互作用以各种方式改善了我们的福祉,如上所述。
Cited references Biological Seminar代写
- Hammen, V.C., and J. Settele. “Biodiversity and the Loss of Biodiversity Affecting Human Health.” Encyclopedia of Environmental Health, 2019, 340-350. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-409548-9.11585-4.
- Jonathan, Marks. “Health and Human Populations.” Human Biodiversity, 2017, 203-218. doi:10.4324/9780203789605-11.
- Lloyd, Pauline. “Sustainable agriculture for biodiversity, biodiversity for sustainable agriculture.” Biodiversity18, no. 2-3 (2017), 124-125. doi:10.1080/14888386.2017.1366873.
- McShane, KATIE. “WHY ANIMAL WELFARE IS NOT BIODIVERSITY, ECOSYSTEM SERVICES.OR HUMAN WELFARE: TOWARD A MORE COMPLETE ASSESSMENT OF CLIMATE IMPACTS.” Les ateliers de l’éthique13, no. 1 (2018), 43. doi:10.7202/1055117ar.
- Stinner, Deborah. “Biodiversity: Agriculture.” Terrestrial Ecosystems and Biodiversity, 2020, 17-21. doi:10.1201/9780429445651-3.
- Zhang, Zhenguo, and Jun Zhou. “From ecosystems to human welfare: the role and conservation of biodiversity.” Ciência Rural49, no. 5 (2019). doi:10.1590/0103-8478cr20170875.



