Does a strong organizational culture increase the overall performance of a firm?
organizational culture代写 With the development of the globalization, the successful establishment of organization culture becomes vital
1.Introduction organizational culture代写
With the development of the globalization, the successful establishment of organization culture becomes vital to help the firm adapt to the complex and volatile environment and form its own core competitiveness in the market competition. Organizational culture impacts the life and working conditions of employees, guides the professional behavior of employees and support the development of enterprises. In other words, organizational culture influences the performance of the company in almost every aspects of business operations.
Academic researches show that there is indeed a significant correlation between organizational culture and corporate performance, but there are no systematic studies which explore the mechanism of organizational culture affecting corporate performance, especially for Chinese enterprises. Inspired by the research gap, this essay aims to enrich the study of organizational culture’s impact on corporate performance regarding Chinese enterprises through literature analysis and case study.
This essay takes a Chinese company,
Huawei, as an example to analyze whether a strong organizational culture increases the overall performance of the firm. More specifically, the essay applies Denison model (Denison & Mishra, 1995) to Huawei’s case in analysis.organizational culture代写
The essay is organized as follows. The second section introduces the real world problems to be addressed. Section three presents Denison model and section four carries out the analysis using Denison model. The final fourth section gives conclusions based on previous analysis.
2.Real World Problems of Huawei
Based in china, Huawei is a leading global provider of information and communications technology infrastructure and smart services. As of 2018, Huawei has operations in more than 170 countries and regions and a customer base of over 3 billion people (Huawei, 2019). Deeply involved in global market, Huawei is confronted with complicated external environment, such as varied customer demands, complicated supply chain with suppliers in different countries, worldwide competitors, various pressure groups and complex general environment regarding economic, legal, political, sociocultural, demographic, technological and global conditions.
The multi-national factorsin external environment brings numerous problems for Huawei.
According to a list of core suppliers recently released by Huawei in 2019 Huawei Core Supplier Conference in Shenzhen, China, Huawei’s 92 core suppliers are from 11 different countries and regions: 33 of them come from the United States (such as Intel, Qualcomm, Broadcom), 25 are Chinese companies (such as Luxshare Precision, BYD, BOE Technology, AAC Technologies, SF Express), the rest of them scatter in Japan, Taiwan, Germany, Switzerland, South Korea, Hongkong, Netherlands, France and Singapore (ESM China, 2019). The suppliers’ international background fortifies the impacts of general environment on Huawei.
One example is the recent trade conflict between China and US, which influences several conditions of Huawei’s external environment. First, economic conditions: Chinese RMB depreciates against US dollar from 6.5 in the beginning of 2018 to 7.1 as of October 25th, 2019 (Bloomberg, 2019), increasing US purchasing costs and reducing the RMB measured profits of products and services sold in the US. Second, political/legal and supplier conditions: US Bureau of Industry and Security added Huawei and sixty-eight its non-US affiliates to the Entity List effective May 16,
2019 (Federal Register, 2019), several US suppliers and partners,organizational culture代写
such as Google, Intel, Qualcomm, Arm and AMD suspended part of cooperation with Huawei (later resumed), negatively affecting Huawei’s supply china and product manufacture. Third, technological conditions: Huawei was blocked by several technology organization, such as JEDEC (Solid State Technology Association), Wi-Fi Alliance, and SDA, hindering technical exchange and cooperation within the industry. Fourth, customer conditions: customers are unable to use Google Play, Gmail, YouTube and Chrome on Huawei’s new phones due to Google’s ban, adversely impacting consumers’ purchasing behavior.
Exposed to the complicated and volatile external environment, one small unfavorable change in a single condition can lead to a negative chain reaction among other conditions under external environment. Thus, a strong organizational culture is needed to help the company better handle these challenges.
3.Organizational Culture and the Denison Model organizational culture代写
The study of organizational/corporate culture began in the 1980s and its theoretical development can be roughly divided into two groups. The first group of researchers mainly focus on theoretical research and reflection. Scholars investigate basic theories and study the concepts, components, and types of organization culture. For example, Peters and Waterman (1982) holds that corporate culture is formed when employees make a certain contribution in the enterprise, get a sense of purpose, love work, have passion and motivation for work, and hope to be recognized. Ouchi and Cuchi (1981) proposes that corporate culture consists of tradition, style and values.
Denison and Deal Terrence and Kenneddy (1982) analyzes the five components of corporate culture:
values, corporate environment, outstanding heroes, rituals, and cultural networks.Kotter and Heskett defines corporate culture as the values and business philosophy held among the managers and employees of a firm. Denison and Mishra (1995) believes that corporate culture is the values and beliefs that are shaped together within the enterprise; it has a series of standard demonstrations, and practices and actions that reinforce these fundamental principles. Robbins and Judge (2007) believe that corporate culture is gradually formed in long-term activities of employees and corporate culture can promote employees’ common values and behaviors. Generally, corporate culture is usually defined as belief, values, ethics, code of conduct and so on where corporate culture is a set of values and concepts.
As for the second group,
corporate culture researches are no longer limited to theoretical researches,but also extend to the measurement, diagnosis and evaluation of corporate culture. Scholars have developed a number of scales and measurement tools for quantitative assessments and diagnostics of corporate culture and quickly apply them to practice. For example, Quinn and Rohrbaugh (1983) conclude that the corporate culture is composed of strategy and intention, employee-work, leadership style and organizational structure after a large amount of literature and empirical researches.
Dimensional composition Hofstede develops Multidimensional Model of Organizational Culture (Hofstede et al., 1990), divide the values of corporate culture into center on work, demand for authority and demand for security, and on this basis, streamline five dimensions: right needs, employees and work, attention to results, security, openness and regulation. O’Reilly and Chatman (1991) establish seven dimensions to measure corporate culture: innovation, stability,organizational culture代写
respect for employees, attention to results, attention to detail, proactive attitude and team attention.
On the basis, the respondent first describes the actual perceived organizational culture, then describes the required organizational culture, and compares the two. Denison and Mishara (1990) hold that corporate culture consists of a series of values, beliefs and behavioral patterns and has four cultural characteristics (named as Denison Model afterwards): adaptability, mission, consistency and involvement. Each cultural dimension corresponds to three sub-dimensions. The content of the scale includes: adaptability (innovation change, customer orientation, organizational learning), mission (strategy and intention, goal, vision), consistency (core values, coordination, integration), involvement (authorization, team orientation and ability development).
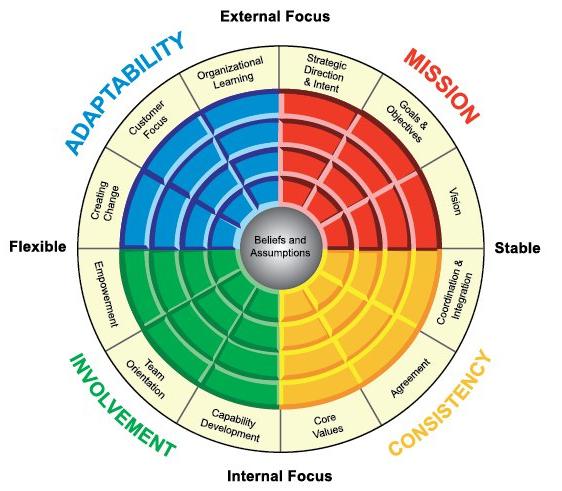
Denison Model
Denison Consulting. (n.d.).
This essay adopts the Denison Model dimension for its multiple advantages. First, the scale contains many sub-dimensions and reveals corporate culture content in very detail. Second, the scale attaches great importance to the enterprise practice application: its has been used widely in both empirical analysis academically (see Denison et al, 2004; Denison and Ward, 2004; Fey and Denison, 2003) and in the real world by Denison Consulting to serve worldwide consumers.
4.Analysis
Mission
As stated in the annual report, Huawei’s mission is to bring digital to every person, home and organization for a fully connected, intelligent world. This strategic direction and intent are widely understood and accepted within Huawei’s employees, ensured by short-term performance appraisal of project goals and objectives and motivate employees to move on. Besides, Huawei has mandatory training for new employees in military-formed community to strengthen then learning of corporate culture. Also, Huawei publishes corporate publications to illustrate the basic principle of Huawei with various basic codes of conduct. For example: dress code, customer go first in elevation, lady first, double-usage of the draft paper. Through the textualization, Huawei adheres to the cultivation of corporate culture to ensure the mission is shared within the company.
Adaptability
Adaptability examines Huawei’s ability to translate external environment demands into action. Huawei performs well in terms of adaptability: employees are aware of external environment change, committed to responding to customers’ every needs and organizational learning are attached to great importance. Huawei’s corporate culture emphasizes that the company relies on customers and adheres to customer-centricity to create value for customers through innovative products. Meanwhile, as for leaning, Huawei build a win-win ecosystem with suppliers, partners, industrial organizations, open source communities, standards organizations, universities, research institutions, etc to promote technological progress and industrial development.
Involvement organizational culture代写
Huawei des excellent job regarding involvement: the company is owned by the employees where 100% ownership belongs to the employees. Huawei’s culture emphasizes that the company relies on hard-working employees and contributors are promised to get a reasonable return. Correspondingly, Huawei implements the employee stock ownership plan through the labor unions. The number of participants were 96,768(Huawei, 2019) and all the participants are employees of the company with no government departments or institutions. The employee stock ownership plan makes employees feel involved in the everyday working, encourage teamwork more effectively due to common interests, make employees feel invested.
Consistency
Huawei has great consistency in corporate culture.
Since the establishment in 1987, Huawei’s core values have been customer-centered, struggle-oriented, working hard and sticking to self-criticism. Meanwhile, Huawei is able to reach agreement when issues arise, which is ensured by Huawei’s highest authority of the company, shareholding employee representative union, that make decisions on major issues such as profit distribution, capital increase and election of directors and supervisors.
Huawei has outstanding performance in corporate culture, measured through the four dimensions under Denison Model, which enhances the overall performance of the company. Financially, Huawei’s annual revenue surpassed US$100 billion for the first time (Huawei, 2019), achieving continuous increases in revenue, operating profit and net profit since 2013. Culturally, employees share the same mission, have good adaptability, join great involvement and performs well in consistency. For example, during the recent China-US trade conflict when Huawei has difficulty accessing some of the raw materials and technology due to the ban from suppliers and partners, Huawei’s employees are even willing to overtime for free for the company to overcome the difficulties.
5.Conclusion organizational culture代写
Through the case study of Huawei, the essay concludes that organizational culture does increase the overall performance a firm. More specifically, organizational culture has an effect on corporate performance through four dimensions: mission, involvement, adaptability and consistency: widely understood and accepted mission helps the company move in the right direction efficiently, deep involvement of employees ensure effective contributions, adaptability facilitate the company to deal with changing external environments and consistency reduces conflict among employees when issues arises. By this way, Huawei’s culture improves the overall performance of the company, both financially and culturally.
References
Bloomberg (2019). USDCNY: CUR. Retrieved from https://www.bloomberg.com/quote/USDCNY:CUR.
Deal Terrence, E., & Kenneddy, A. A. (1982). Corporate cultures: The rights and rituals of corporate life.. e. ading. MA: Addison-Wesley. p.
Denison Consulting. (n.d.). Retrieved from https://www.denisonconsulting.com/docs/CultureGettingStarted/The_Denison_Model.htm
Denison, D. R., Haaland, S., & Goelzer, P. (2004). Corporate culture and organizational effectiveness: Is Asia different from the rest of the world?. Organizational dynamics, 33(1), 98-109.
Denison, D., Lief, C., & Ward, J. L. (2004). Culture in family-owned enterprises: Recognizing and leveraging unique strengths. Family Business Review, 17(1), 61-70.
Denison, D. R., & Mishra, A. K. (1995). Toward a theory of organizational culture and effectiveness. Organization science, 6(2), 204-223.
ESM China (2019 November 30). Huawei announces 92 core supplier lists for the first time. Retrieved from https://www.esmchina.com/news/4477.html
Federal Register (2019 August 21). Addition of Certain Entities to the Entity List and Revision of Entries on the Entity List. Retrieved from https://www.federalregister.gov/documents/2019/08/21/2019-17921/addition-of-certain-entities-to-the-entity-list-and-revision-of-entries-on-the-entity-list.
Fey, C. F., & Denison, D. R. (2003). Organizational culture and effectiveness: can American theory be applied in Russia?. Organization science, 14(6), 686-706.
- Hoforede, B. Neuijen, D.D. Ohayv, & G. Sanders. (1990). Measuring organizational culture and effectiveness. Organization science,204-223.
Heskett, J. L., & Kotter, J. P. (1992). Corporate culture and performance. Business Review. Vol, 2(5), 83-93.
Huawei. (2019). Huawei Investment & Holding Co., Ltd. 2018 Annual Report. Retrieved from https://www.huawei.com/us/press-events/annual-report/2018
O’Reilly III, C. A., Chatman, J., & Caldwell, D. F. (1991). People and organizational culture: A profile comparison approach to assessing person-organization fit. Academy of management journal, 34(3), 487-516.
Ouchi, W. G., & Cuchi, W. G. (1981). Theory Z: How American business can meet the Japanese challenge (Vol. 13). Reading, MA: Addison-Wesley.
Peters, T. J., Waterman, R. H., & Jones, I. (1982). In search of excellence: Lessons from America’s best-run companies.
Quinn, R. E., & Rohrbaugh, J. (1983). A spatial model of effectiveness criteria: Towards a competing values approach to organizational analysis. Management science, 29(3), 363-377.
Robbins, S. P., & Judge, T. A. (2007). Organizational culture. Organizational behavior, 28-50.

更多其他:prensentation代写 文学论文代写 商科论文代写 艺术论文代写 Essay代写 研究论文代写 期末论文代写 毕业论文代写 论文代写




您必须登录才能发表评论。