1.
free trade equilibrium代写 a. For the excess supply curve is P=100+4X ,and the world price ratio Px/Py is P=200. Substitute 200=100+4X
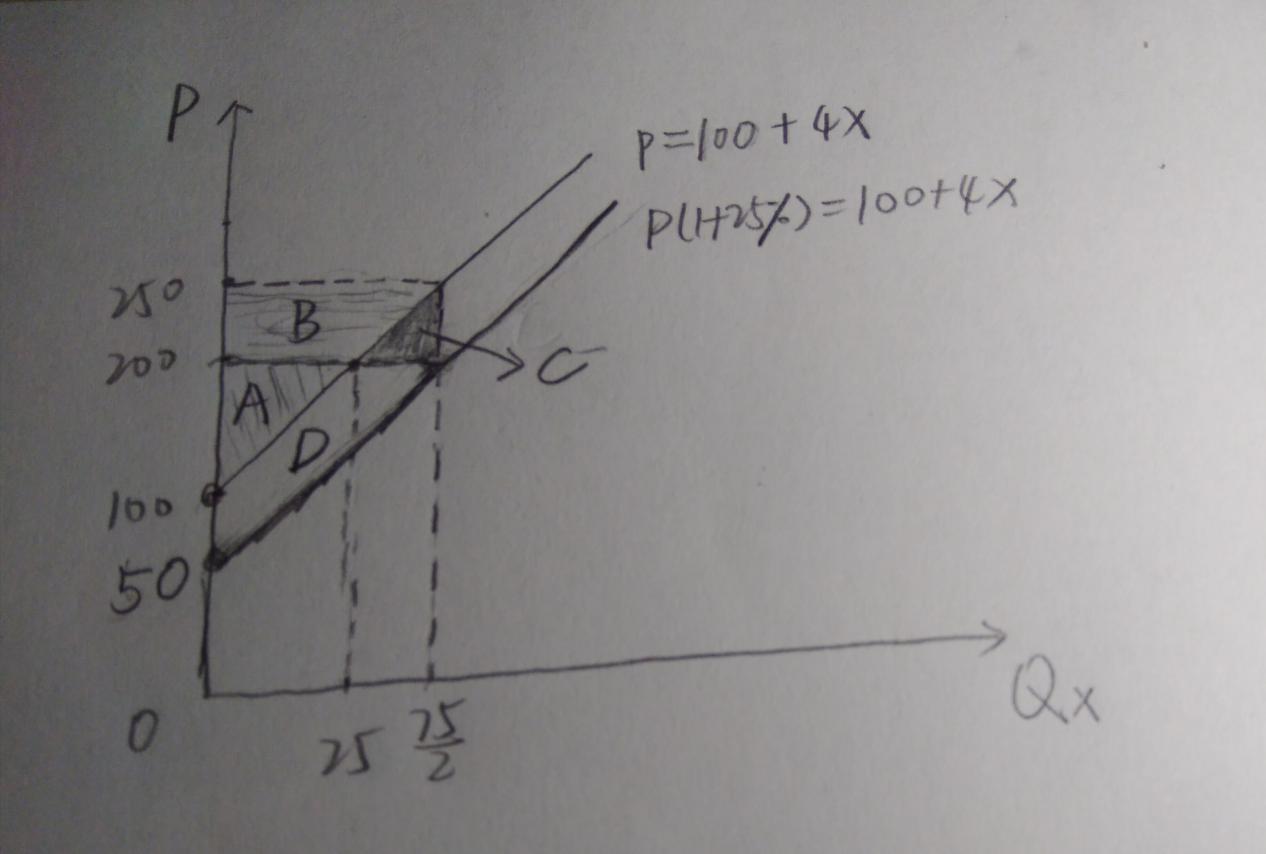
a.For the excess supply curve is P=100+4X ,and the world price ratio Px/Py is P=200. Substitute 200=100+4X , then X=25. So the free trade equilibrium quantity of exports is 25.
b.The producer surplus equals the area of the triangle A in the graph. free trade equilibrium代写
Producer surplus = 1/2 ( 200 – 100 ) * 25 = 1250
C.When country H elects to offer a 25% subsidy to exports of X. Then the equilibrium price will be P’=P(1+25%) , and the supply curve is P’=100+4X .
Substitute 250=100+4X ,then X=75/2 so the equilibrium quantity of exports with this subsidy is 75/2.
D.The new producer surplus equals the area of the triangle A plus D in the graph.
Producer surplus = 1/2 ( 250 – 100 ) * 75/2 = 2812.5
E.The government expenditure on the subsidy equals the area of B plus C in the graph. government expenditure=(250-200)*75/2=1875
F.H’s deadweight loss due to the subsidy equals the area of the triangle C in the graph.
deadweight loss =C=1/2(75/2-25)(250-200)=312.5 free trade equilibrium代写
2. free trade equilibrium代写
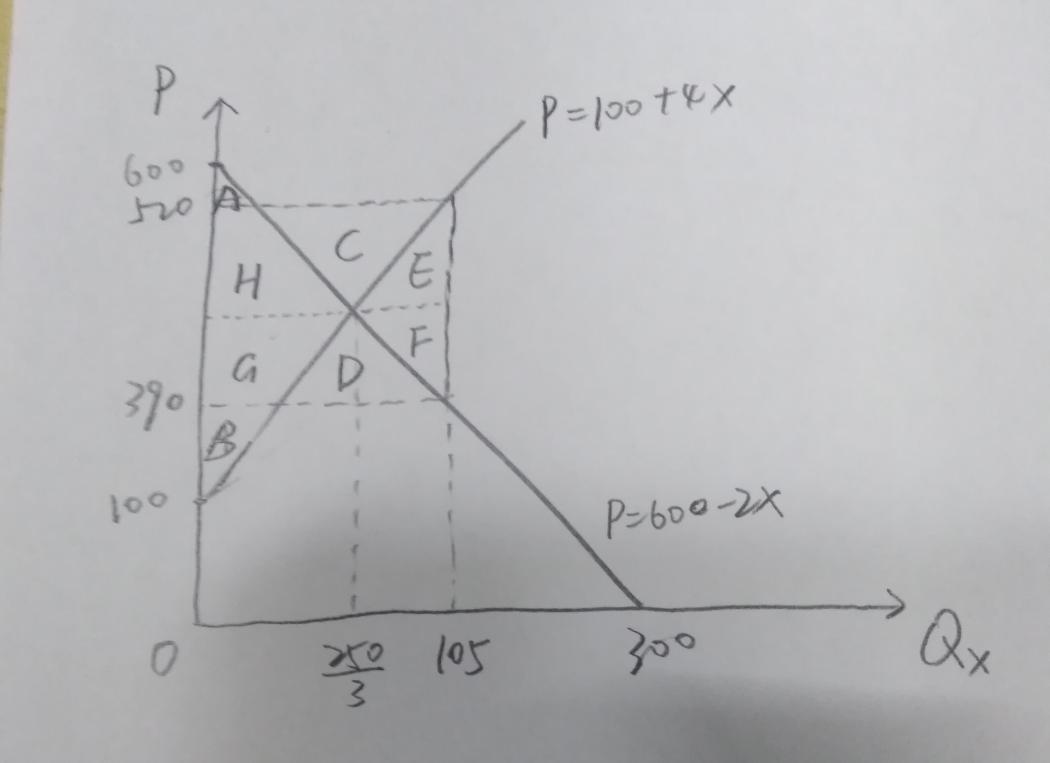
A.For its excess supply curve is P=100+4X. And the world’s excess demand curve for X is P=600-2X. Substitute 100+4X=600-2X, then the equilibrium quantity of X is 250/3, and the equilibrium price is 1300/3.
B.The producer surplus equals the area of the triangle B plus G in the graph.
Producer surplus = 1/2 ( 1300/3 – 100 ) * 250/3 = 125000/9
C.For the excess supply curve is Ps=100+4X ,and the excess demand curve is Pb=600-2X .And country H elects to offer a 25% subsidy to exports of X. Then Ps -Pb =25%Ps , substitute 0.75(100+4X)=600-2X, then the equilibrium quantity of X is 105.
D.The new producer surplus equals the area of the triangle B plus G and D in the graph.Ps=100+4X=520, Pb=600-2X=390.
Producer surplus = 1/2 ( 520 – 100 ) * 105 =22050
E.The government expenditure on the subsidy equals the area of GHCDEF in the graph. government expenditure=(520-390)*105=13650
F.The deadweight loss due to the subsidy equals the area of the triangle EF in the graph.
deadweight loss=1/2(520-390)(105-250/3)=4225/3
G.Terms of Trade=N=(P1 / P0)÷(q1 / q0)*100%
=(520/1300/3)/(390/1300/3)*100%=133.33%
ΔN=N-100%=33.33%
3.
A.False. Import substitution growth is a strategy of substituting domestic products for imports, or of promoting industrialization by restricting the import of manufactured goods.It needs a lot of resources in the country.What’s more ,it needs trade protection policy. But export-driven growth means that a country has taken various measures to promote the development of the export oriented industrial sector, replacing the traditional export of the primary products with the non traditional export products, expanding foreign trade and diversifying the export products to promote the development of industry and the economy as a whole. It will make full use of foreign resources, and its implementation needs loose trade policy. So it’s contradictory for a country to simultaneously engage in import substitution and export-driven growth. free trade equilibrium代写
B.False. If a country adopts an import substitution strategy, that is, for the goods X, the state will adopt a trade protection policy to restrict the import of X to provide protection and development conditions for the production of X of its own goods. But it is not necessarily a subsidy to the export of X. Similarly, the country’s export oriented strategy will subsidize the X of goods, but not necessarily impose tariffs.
4.free trade equilibrium代写
In general, the tariff policy of a country refers to a country’s tariff standards which in order to protect and promote the development of its national economy, to guarantee the national tariff income and to realize the economic development target in a certain period by means of tariff . The tax law on plastic bottled water in the United States at this time is not for those reasons, but to protect the environment from the domestic consumption of plastic bottled water. However ,as long as the tax on plastic bottled water is exist and even too high, whatever the reason, the result will have the impact of tax policy.
For the United States, the tax law means the U. S. restrictions on imported plastic bottled water from foreign countries, especially Fiji, which will lead to less Fiji’s plastic bottled water exports to the United States and more support for its own plastic bottled water production companies and the demand for bottled water to domestic producers in the U.S. This result can not solve the environmental pollution caused by plastic bottled water. In addition, Fiji has a comparative advantage in producing plastic bottled water, and a heavy tax on products that a country do not have a comparative advantage is contrary to the Comparative Advantage Trade Theory.That is, the United States should allow Fiji with comparative advantage to produce plastic bottled water rather than domestic production, which will increase production cost and it’s not conducive to the economic interests of the country.free trade equilibrium代写
For Fiji, the country has the comparative advantage of producing bottled water,
and much of the bottled water is consumed in the United States. So a higher tax on its bottled water imports will increase the cost of Fiji’s exports to the United States. According to the supply and demand theorem, it will eventually reduce the number of final transactions, which will reduce the prducers surplus of Fiji and reduce social welfare. While the United States is the big exporter of products, the quantity of exports in the United States is reduced and the redundant products which unable to complete the transaction due to tariffs are difficult to completely sold to other countries. This will make the Fiji’s bottled water overproduction, which is not conducive to the production link and the circulation of production factors.
In short, from the trade point of view,
the United States imposed tariffs has a not good influence on both countries. The existence of tariffs has reduced the surplus of producers and consumers. Although the United States government has a part of the tax revenue, it can not make up for the decrease of welfare, resulting in the deadweight loss caused by tax. The international trade benefits of both sides of trade have been reduced, and the situation of both countries has not been better.
But apart from trade, we can also consider externalities. The original purpose of this Law in the United States is to protect environment, and the imposition of tariffs undoubtedly brings positive externalities to environmental protection. First of all, the existence of tariff does make the consumption of plastic bottled water less, which can directly reduce its environmental pollution. Secondly, as the United States does not have a comparative advantage in producing bottled water, it will enable American companies to create environmentally friendly alternatives of bottled water with relatively comparative advantages. Finally, as exports to the US decrease, Fiji will reduce the production of bottled water in accordance with the new equilibrium of supply and demand. The positive externalities brought about by these actions will increase social welfare.
更多其他:prensentation代写 文学论文代写 商科论文代写 Essay代写 研究论文代写 期末论文代写 毕业论文代写 论文代写




您必须登录才能发表评论。