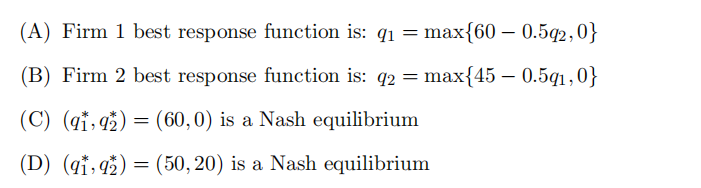ECON7070
Practice Test 2
ECON Test代写 Test 2 will be a combination of questions like the ones in tutorials 4,5,6 and the following questions.
Test 2 will be a combination of questions like the ones in tutorials 4,5,6 and the following questions.
1 Which is true for the following two-player game: ECON Test代写
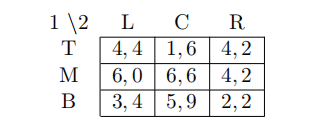
(A) T is a best response to L
(B) (M,C) is the only Nash equilibrium
(C) (M,R) is a Nash equilibrium
(D) There is a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in which player 2 chooses both C and R with positive probability
2 Which is false for the following game?
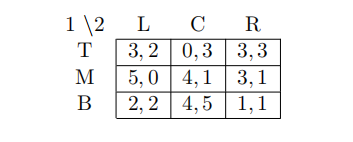
(A) (M,C) and (B,C) are the only pure strategy Nash Equilibria
(B) There is a Nash equilibrium in which R is played with positive probability
(C) There is no Nash equilibrium in which L is played with positive probability
(D) There is no Nash equilibrium in which both players choose two of their actions with positive probability
3 Which is true for the following game?
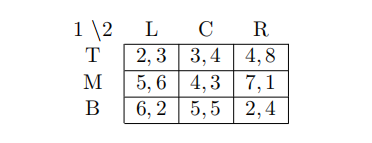
(A) There is a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in which Player 1 plays both M and B with positive probability and Player 2 plays both L and C with positive probability
(B) The best response of Player 2 to M is C
(C) (B,C) is the only Nash equilibrium
(D) (M,L) is a Nash equilibrium
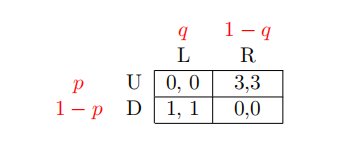
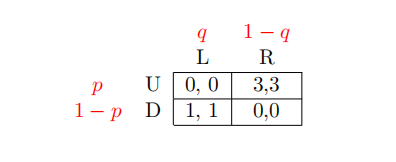
4 In the following game, in which s1 = (p, 1 − p) is Player 1’s strategy and s2 = (q, 1 − q) is Player 2’s strategy, Player 1 is indifffferent between U and D when q is equal to: [Write you answer as a decimal number, e.g. 0.33]
5 In the following game, in which s1 = (p, 1 − p) is Player 1’s strategy and s2 = (q, 1 − q) is Player 2’s strategy, Player 2 is indifffferent between L and R when p is equal to: [Write you answer as a decimal number, e.g. 0.33]
6 Which is true for the following game? ECON Test代写
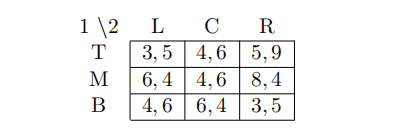
(A) (T,R) is a Nash equilibrium
(B) There is a Nash equilibrium in which Player 1 plays M and B with equal probability and Player 2 plays each action L, C and R with positive probability
(C) There is a Nash equilibrium in which Player 1 plays each action T, M and B with positive probability and Player 2 plays each action L, C and R with positive probability
(D) There is a Nash equilibrium in which Player 1 plays M and B with equal probability and Player 2 plays L and C with equal probability
7 The following game:
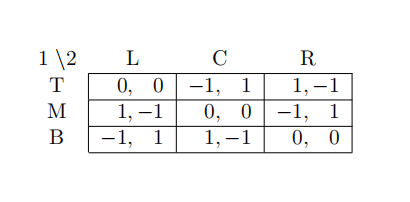
(A) Has a pure strategy Nash equilibrium
(B) Has a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in which Player 1 plays T, M and B with equal probability and Player 2 plays L C and R with equal probability
(C) Has a mixed strategy equilibrium in which Player 2 only puts positive probability on L and R
(D) Has a mixed strategy Nash equilibrium in which Player 1 plays M and B with probability 0.5 each and Player 2 plays L and C with probability 0.5 each
8 If Player 2 chooses L and R with equal probability and Player 3 chooses A and B with equal probability, then Player 1 best response is: ECON Test代写
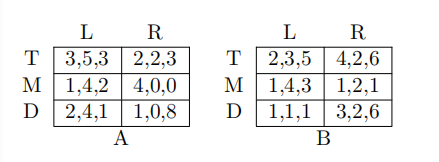
(A) T
(B) M
(C) D
(D) Both M and D
9 In the following game, if Player 2 chooses L and R with equal probability and Player 1 chooses M, then Player 3’s expected utility from choosing A is:
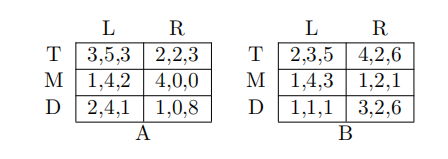
10 Which is false for the following three player game?

(A) (D,T,T) is a Nash equilibrium
(B) (T,D,D) is a Nash equilibrium
(C) (T,D,T) is a Nash equilibrium
(D) None of the players has a dominant strategy
11 Which is false for the following game? ECON Test代写
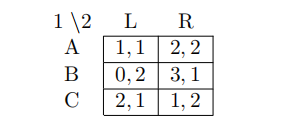
(A) It has no pure strategy Nash equilibrium
(B) There exists a Nash equilibrium in which player 1 plays B with zero probability
(C) There exists a Nash equilibrium in which player 1 plays C with zero probability
(D) There exists a Nash equilibrium in which player 1 plays A with zero probability
12 Let s1 = (pT , pM, pB) be the strategy of Player 1 (with pi the probability of action i) and s2 = (qL, qC, qR) be the strategy of Player 2 (with qi the probability of action i). Which is false for the following game?
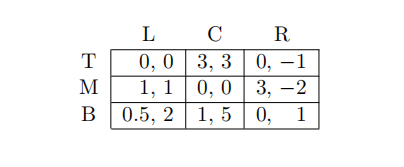
(A) (M,L) and (T,C) are the only pure strategy Nash equilibria
(B) s1 = (0.5, 0.5, 0) and s2 = (0.5, 0.5, 0) is a Nash equilibrium
(C) s1 = (0.25, 0.75, 0) and s2 = (0.75, 0.25, 0) is a Nash equilibrium
(D) In any strictly mixed strategy equilibrium, Player 1 puts positive probability on T and M only, and Player 2 puts positive probability on L and C only
13 Consider a simultaneous move game played by two players, Player 1 and 2. Player i’s action set is ti ∈ [0, ∞) and the utility function of player i is
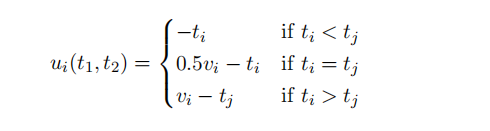
where i ≠j and v1 = 20, v2 = 10. Which of the following is not a pure strategy Nash equilibrium of this game?
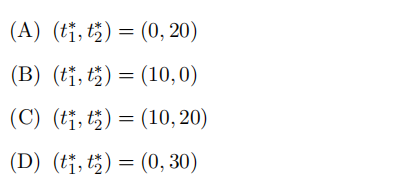
14 Consider a Cournot duopoly. The market demand function is P = 130 − (q1 + q2), where P is the market price, q1 is the output produced by Firm 1 and q2 is the output produced by Firm 2. The two fifirms have a constant marginal cost c = 10. The pure strategy Nash equilibrium of this game is:
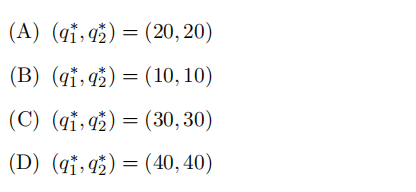
15 Consider a Cournot duopoly. The market demand function is P = 130 − (q1 + q2), where P is the market price, q1 is the output produced by Firm 1 and q2 is the output produced by Firm
- Firms 1 have a constant marginal cost of c1 = 10, while Firm 2 has a constant marginal cost of c2 = 40. Which is false?