BHM 363 – Managing and Interpreting Financial Information
Financial代考 Your portfolio should be built up and completed within this document. It contains the following elements:
Your portfolio should be built up and completed within this document.
It contains the following elements:
- what do you want from the module?
- statement of financial position – item ordering
- ratio calculations
- costing exercise
- budgeting exercise
- interpreting a business case
- creating a business case
- short reflection
Ethical declaration Financial代考
I declare that I will personally prepare this portfolio and that it has not in whole or in part been submitted for any other degree or qualification. The work included here will be my own, carried out personally by me unless otherwise stated.
I will acknowledge any sources of information, including quotations, by means of reference, both in a final reference section, and at the point where they occur in the text.
I understand that plagiarism and collusion are regarded as offences against the University’s Examination Regulations and may result in formal disciplinary proceedings. If I need help to understand or answer the questions I will contact appropriate Aston staff, not fellow students or any other contacts.
1. What Do You Want From The Module? Financial代考
Clearly there is no right or wrong answer to this section. It should be completed early in the module, after section 1. Introductions. It is intended to help you when you complete the reflection at the end.
Please think about this for a few minutes and make some BRIEF notes…(bullet points are fine)
- About yourself…include any experience you have in financial reporting, management reporting, or accounting.
- At the moment, how much do you expect to need to use financial information at work in future? Do you have any idea what sorts of things you might need to do?
- What do you hope to get out of this module?
People tend to learn better if they have intrinsic motivations for learning, not simply passing to help get CIPD accreditation. Can you think of reasons you are going to be intrinsically motivated during this module? Do you simply enjoy learning? Will the content be useful to you? Are you curious about it?
My notes:
2. Statement of Financial Position – Item Ordering Financial代考
For completion after section 2. Financial Statements.
First copy the names of the sections of a Statement of Financial Position (otherwise known as a Balance Sheet) into the correct (shaded) places in the simplified statement table on the next page.
Total equity Non current assets
Current liabilities Non current liabilities
Equity Current assets
Net assets Total assets
Total liabilities
Now put the following balance sheet elements and their values into the statement in an appropriate order, checking that they balance. You may add category subtotals if that helps. Calculate and highlight the two totals that must balance: Financial代考
| Retained Profits | 250 | Land And Buildings | 200 | |
| Trade & Other Payables | 60 | Plant And Equipment | 130 | |
| Debentures | 40 | Share Premium Account | 30 | |
| Ordinary Share Capital | 120 | Inventory | 110 | |
| Receivables | 70 | Bank Overdraft | 10 |
Please complete the Simplified Statement of Financial Position Table
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. Ratio Calculations Financial代考
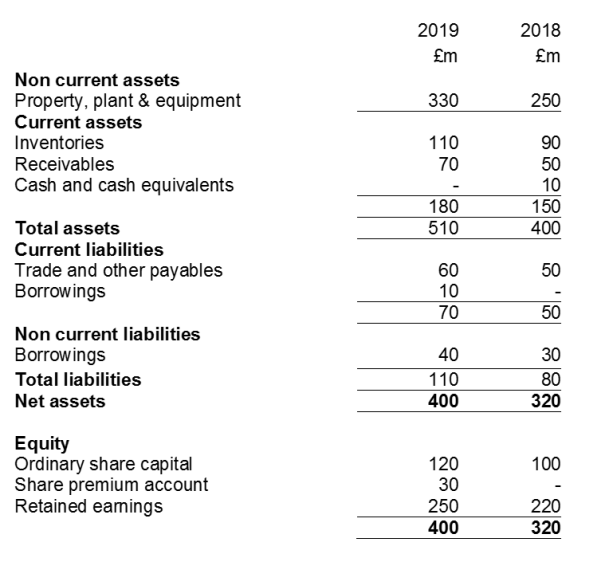
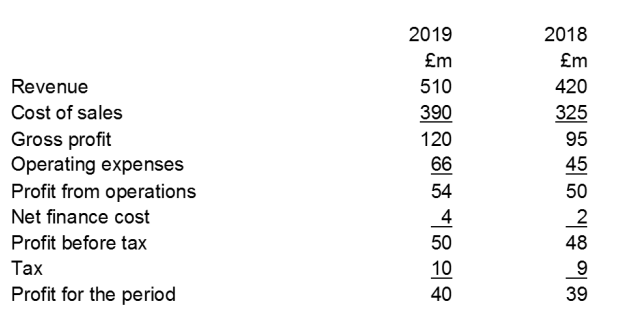
Please calculate the following key ratios for XYZ Ltd in 2019 to complete the table below. The XYZ Ltd Statement of Financial Position (otherwise known as the Balance Sheet) and Statement of Profit or Loss (or Income Statement) are on the following pages to provide the information you will require.
| XYZ Ltd: Key Ratios | |||||
| 2019 workings | 2019 | 2018 workings | 2018 | ||
| Profitability | |||||
| Return on capital employed | =50/(350) x 100 | 14.3% | |||
| Return on sales (Operating margin/EBIT margin) | =50/420 x 100 | 11.9% | |||
| Gross profit margin | =95/420 x 100 | 22.6% | |||
| Efficiency | |||||
| Sales revenue on capital employed | =420/350 | £1.20 | |||
| Liquidity | |||||
| Current ratio | =150/50 | 3.00 | |||
| Acid Test (Quick ratio) | =(150-90)/50 | 1.20 | |||
| Solvency/Stability | |||||
| Gearing | * | =30/350 x 100 | 8.6% | ||
| Interest cover | =50/2 | 25.00x | |||
| * Debt includes short term as well as long term borrowings |
XYZ Ltd Statement of Financial Position
XYZ Ltd Statement of Profit or Loss
4. Costing Exercise
– Painting job cost variance analysis Financial代考
Your decorating company is doing a fixed price painting job for a customer. You worked out the fixed price using the company’s normal standard costs for the size of job, which should take 2 people 5 days. When he returns, the senior decorator tells you he had managed to complete the job OK, but he had had to deal with problems because his assistant had gone off sick, and the warehouse hadn’t had the usual paint in the right colour, so he had to use some more expensive stuff. You wonder how this will have affected the costs, and hence profit, for the job.
The Standard costs for the 5 day job are:
Materials 50 litres at £2.19/litre =
Labour Senior decorator 40 hours at £10/hour =
Junior decorator 40 hours at £7.50/hour =
The Actual costs for the 5 day job were: Financial代考
Material 25 litres at £ /litre = £375
Labour Senior Decorator 40 hours at £ /hour = £400
Junior Decorator 4.6 hours at £ /hour = £34.50
a.What is the overall difference in total cost between the standard and actual costing?
b.Calculate all 3 material variances
Total Material Cost Variance = Total Standard Cost Materials
– Total Actual Cost Materials
= adverse/favourable (delete as appropriate)
Material Price Variance = (standard price/litre x actual litres used)
– Total Actual Cost Materials
= adverse/favourable (delete as appropriate)
Material Usage Variance = Total Standard Cost Materials
– (standard price/litre x actual litres used)
= adverse/favourable (delete as appropriate)
The 3 labour variances are as follows: Financial代考
Total Labour Cost Variance = £265.50 (favourable)
Labour Rate Variance = £0
Labour Efficiency Variance = £265.50 (favourable)
c.Briefly explain in words rather than numbers what the 6 variances above show you about this job.
d.Can you think of any further questions you might ask, and can you see any possible actions you might take as a result? (For example, what difference might using a more expensive paint have made? Might this explain the variances? Think about what you might expect from an expensive rather than very cheap paint in real life. How could you check your hypothesis?)
5. Budgeting Exercise Financial代考
Your manufacturing company has very seasonal, but predictable, sales. However it is more efficient and effective to manufacture at a steady rate throughout the year, so its normal costs are a steady £120,000 a month. Your company needs to buy some new equipment costing £300,000 fairly soon, but you don’t want to borrow any money to do it. You draw up a cash budget for the next year (January to December) to see when you can afford to buy it without going overdrawn on your bank account at any point in the year.
You are starting the year with £60,000 cash from 31st December.
Your cash flow forecast table is below. Fill in the missing end of month / start of month bank balances.
| In £,000 | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec |
| Start of month | 60 | |||||||||||
| Cash Income | 200 | 108 | 65 | 233 | 283 | 74 | 32 | 36 | 300 | 239 | 250 | 248 |
| Normal Costs |
120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| End of month |
Which is the first month you think you can buy the new equipment at the start of the month WITHOUT overdrawing the bank account later in the year?
Month Financial代考
Please test your hypothesis by adding the cost of the new equipment into the correct month the table below, and completing it again.
| Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | |
| Start of month | 60 | |||||||||||
| Cash Income | 200 | 108 | 65 | 233 | 283 | 74 | 32 | 36 | 300 | 239 | 250 | 248 |
| Normal Costs |
120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 | 120 |
| New Equipment | ||||||||||||
| End of month |
If you got the month wrong, try again.
What is the correct month:
If you got the month wrong originally, can you see why now? If you can’t please ask for help.
Note: if you can use a spreadsheet to do the calculations, copying the table over, then the values back, you can do this exercise much more quickly.
6. Interpreting a Business Case – Oblong Company product plans Financial代考
Oblong Company is a well-established UK company with a stable workforce. It currently produces 2 products, but costs are too high for the current level of sales, and the Operations and Finance Directors have been working together on a plan to increase efficiency and reduce the variable costs for both products by 10%. Fixed costs are allocated 50:50 to the two products because they use equal equipment in the factory. The costs considered as ‘fixed’ are those that could not be changed in the medium term period being considered here, while staff costs could. Unfortunately the plan will mean having to reduce the number of staff.
One of the two Product Managers has proposed an alternative plan – an idea to manufacture a new product. The efficiency changes could be made as planned, but instead of reducing staff, the staff would move to work on the new product instead. It could be made with the existing machinery, using spare capacity. Overall fixed costs would remain the same but a share of them would go to product C in proportion to the capacity used. The variable costs for C would be the same as the total variable cost savings planned for products A and B. The sales manager thinks the company could sell £18 million of new product sales to existing clients, as it would improve the overall package the company offers to them.
You are the HR Director. You will be attending a board meeting to help decide whether to simply make savings, or to also manufacture the new product as well. The Finance Director has circulated a financial summary to help board members to prepare. Remember, you should take into account your own knowledge in HR as well as the financial information provided when making decisions. You should not assume that all the information you need will be presented in the business case.
Table 1. The Finance Manager summarises the current costs:
| Product | A £m | B £m | Total £m |
| Sales Revenue |
180 |
162 | 342 |
| Variable Costs |
103 |
94 | 197 |
| Fixed Costs |
68 |
68 | 136 |
| Net Profit/Loss | 9 | 0 | 9 |
Table 2. The costs if the cost cutting measures are put into place (reducing variable costs by 10%) Financial代考
| Product | A £m | B £m | Total £m |
| Sales Revenue |
180 |
162 | 342 |
| Variable Costs |
92.7 |
84.6 | 177.3 |
| Fixed Costs |
68 |
68 | 136 |
| Net Profit/Loss |
19.3 |
9.4 | 28.7 |
Table 3. The costs if the efficiency changes are made and the new product is produced.
| Product | A £m | B £m | C £m | Total |
| Sales Revenue |
180 |
162 |
18 |
360 |
| Variable Costs |
92.7 |
84.6 |
19.7 |
197 |
| Fixed Costs |
68 |
54.4 |
13.6 |
136 |
| Net Profit/Loss |
19.3 |
23 |
-15.3 |
27 |
a.What is a potentially important one-off cost of making the cost savings without making the new product? The Finance Director does not appear to be taking this into account. Financial代考
b.Working out the Contribution of each of the products might help you to make a decision about manufacturing the new product. What would the Contribution be for each of the three products in Table 3?
| Contribution for A = | |
| Contribution for B = | |
| Contribution for C = |
c.The sales revenue of £18m has been suggested by the Sales Manager for sales to existing customers. If you sold more of the product to more people, would that make the financial situation better or worse? Why?
d.Let us assume the Variable Costs for product C could not be reduced further. Sales revenue is calculated by multiplying Price by Number Of Units Sold. So which of these elements needs further research? (If it could be increased, the financial case for product C would look much better.)
e.Assuming the finances of product C could be changed to make a small Contribution, what are some arguments to favour manufacturing product C, even if the organisation’s overall profits would be no greater based on the sales projection of C so far? (Not all arguments have to be financial. Brief bullet points are fine.)
7. Business Case Financial代考
Your organisation – a major multinational corporation – has decided it needs to improve its leader development. The HRM Director asks you to organise the business case for training and development of UK staff.
Please PLAN your business case. (You don’t have to write the case itself. Bullet points are fine).
- How will you go about it?
- What information will you try to find, and if possible, where from?
- What Financial Information would you like to include?
- How might you structure it?
- How long do you estimate it will it take you to write the business case?
- Etc.
Please write here:
8. Reflection – up to 500 words
We hope you will take useful skills away from this workshop that you can use in real life. Please reflect on how you might be able to use the knowledge and skills featured in this workshop (whether you already had them, or have just learned them) in your current role and future roles you aspire to.
Have you met the aims you considered at the start of the module? Do you have any suggestions to improve the module?
THANK YOU!
If you have used any References (you do not have to) please list them below.




