1.1)

GDP代写 the GDP growth rate in 2018 has fallen compared to the former years with several reasons: A. An unbalance of net exports
a. Under the expenditure approach, GDP代写
breaking down the GDP needs the calculation of four elements, C (Consumer spending on goods and services) + I(Investor spending on business capital goods) + G(Government’s expending on goods and services by the government) + net exports(exports minus imports of goods and services).
So on describing the GDP of the Czech Republic in 2018 using the expenditure approach, the GDP growth rate in 2018 has fallen compared to the former years with several reasons: A. An unbalance of net exports (the percentage of import is much higher than export’s) B. A higher inflation rate started from 2017 compared with former years.
b.It is influenced by the increasing inflation rate,
it shows that households in the Czech Republic have to pay more money than last year on a certain product with the increasing inflation rate.
2) a. The General Unemployment Rate is the number of unemployed people as a percentage of the labour force, GDP代写
where the latter consists of the unemployed plus those in paid or self-employment, it always indicates the development of a certain economy, the better development, the lower General Unemployment Rate and vice versa.
But the share of Unemployed Persons means the total of unemployed population and the people unwilling to work constitute a socially inactive population that minuses the labour force. The two concepts contain different people
b. A. GDP continues to grow steadily B.
Household expenditure continues to grow steadily. These two indicators are the proof that the economy of Czech Republic goes well.
3) a. It is a creeping inflation when prices rise 3 percent a year or less. GDP代写
It benefits economic growth. This kind of inflation makes consumers expect that prices will keep going up. That boosts demand. Consumers buy now to beat higher future prices. That’s how mild inflation drives economic expansion.
b. The average nominal wage growth rate is much greater than the inflation rate, indicating that the real wages of workers are rising.
4) Exchange Rate Commitment: CZK/EUR=27/1 GDP代写
5) The Government deficit rate from 2014-2018 had never beyond 3% and the Government debt rate from 2014-2018 had never beyond 60%.
6) a. Monopolistic competition refers to the market phenomenon in which many manufacturers produce and sell similar but different commodities.
Its characteristics are: (1) the number of enterprises is large but the scale is relatively small (2) the products are similar and different from each other, so the demand curve is inclined downwards. (3) The enterprise is not restricted in terms of access, resources can be transferred between industries (4) many small Buyer.
An oligopoly is a market state dominated by a small number of sellers (oligarchs). An oligopoly is a market structure that includes both monopolistic and competitive factors and is closer to a complete monopoly. Its distinguishing feature is that a few manufacturers monopolize the market of a certain industry, which accounts for a high proportion of the total output of the industry, thus controlling the supply of products in the industry.
b.
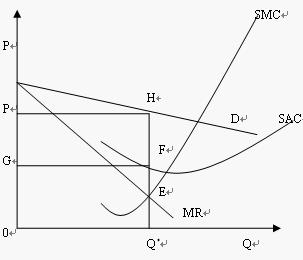
In the process of short-term equilibrium realization, the monopolistic competition market, like the monopoly market, will also have three situations: excess profit, income and expenditure, and loss. The difference from the monopoly market is that the slope of the market demand curve faced by monopolistic competitors is small. After considering the production cost factor, the monopolistic competitor will choose the production under the condition that the marginal cost is equal to the marginal benefit, that is, the E point in the figure below. The output determined by point E is OQ* and the price is OP. Since the short-term average cost at this time is OG, the monopolistic competitor is profitable and its profit is GFHP.
7) a. It indicates that the degree of consumer response to changes in the amount of consumer income over a certain period of time is measured by the coefficient of elasticity. GDP代写
Income elasticity is based on the assumption that the consumer’s preference, the price of the commodity itself and the price of the relevant commodity remain unchanged, analyze the degree of response of the demand for the commodity to the change in income.
Three types of income elasticity of demand
(1)> 1 (luxury, rich income elasticity)
(2) (0,1) (essential, lack of income elasticity)
(3)<0 (low grade)
b. An indicator of the extent to which demand reflects the price change. GDP代写
The formula is the price elasticity of demand = the percentage change in demand / the percentage change in price
When Ed = 0: perfect inelasticity
When 0 < Ed < 1: lacks elasticity, is not elastic, or is inelastic
When Ed = 1: unit elasticity, single elasticity, or unit elasticity
When 1<Ed<+∞ : Elastic
When Ed→+∞: fully elastic or perfect elasticity
c.
A measure of the extent to which a product’s demand responds to changes in the price of its substitute or complement, subject to other conditions.
The cross-elasticity of demand can be positive or negative. The cross-elasticity of the substitute is positive, while the cross-elasticity of the complement is negative.
2.1 A. Balance sheet GDP代写
Assets |
|||||
| Fiscal year is January-December. All values USD millions. | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Cash & Short Term Investments | 21.68B | 19.9B | 22.2B | 20.68B | 15.96B |
| Cash Only | 8.96B | 7.31B | 8.56B | 6.01B | 8.93B |
| Short-Term Investments | 12.72B | 12.59B | 13.65B | 14.67B | 7.04B |
| Total Accounts Receivable | 4.47B | 3.94B | 3.86B | 3.67B | 3.4B |
| Accounts Receivables, Net | 4.47B | 3.94B | 3.86B | 3.67B | 3.4B |
| Accounts Receivables, Gross | 4.8B | 4.29B | 4.32B | 4.14B | 3.89B |
| Bad Debt/Doubtful Accounts | (331M) | (352M) | (466M) | (477M) | (489M) |
Other Receivables |
– | – | – | – | – |
| Inventories | 3.1B | 2.9B | 2.68B | 2.66B | 2.77B |
| Finished Goods | 1.13B | 1.03B | 844M | 693M | 692M |
| Work in Progress | – | – | – | – | – |
| Raw Materials | 1.62B | 1.56B | 1.57B | 1.73B | 1.86B |
| Progress Payments & Other | 351M | 306M | 266M | 233M | 212M |
| Other Current Assets | 3.75B | 6.65B | 5.28B | 9.55B | 8.51B |
| Miscellaneous Current Assets | 3.75B | 6.65B | 5.28B | 9.55B | 8.51B |
| Total Current Assets | 32.99B | 33.4B | 34.01B | 36.55B | 30.63B |
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
| Net Property, Plant & Equipment | 14.63B | 12.57B | 10.64B | 8.2B | 8.23B |
| Property, Plant & Equipment – Gross | 25.26B | 22.35B | 21.26B | 16.45B | 16.25B |
| Buildings | 5.54B | 4.91B | 4.57B | 3.92B | 3.84B |
| Land & Improvements | 972M | 717M | 589M | 334M | 485M |
Computer Software and Equipment |
– | – | – | – | – |
| Other Property, Plant & Equipment | – | – | – | – | – |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 10.63B | 9.78B | 10.62B | 8.25B | 8.01B |
| Total Investments and Advances | 14.69B | 16.81B | 18.46B | 23.49B | 21.69B |
| Other Long-Term Investments | 4.75B | 4.49B | 2.2B | 2.63B | 2.28B |
| Long-Term Note Receivable | – | – | – | – | – |
| Intangible Assets | 26.37B | 24.13B | 21.13B | 16.64B | 17.27B |
| Net Goodwill | 12.1B | 11.29B | 10.63B | 9.4B | 10.26B |
| Net Other Intangibles | 14.27B | 12.84B | 10.5B | 7.24B | 7.01B |
| Other Assets | 3.02B | 2.73B | 2.71B | 2.7B | 2.73B |
| Tangible Other Assets | 3.02B | 2.73B | 2.71B | 2.7B | 2.73B |
| Total Assets | 92.02B | 90B | 87.27B | 87.9B | 83.22B |
| Liabilities & Shareholders’ Equity | |||||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | |
| ST Debt & Current Portion LT Debt | 22.68B | 15.81B | 16.03B | 16.5B | 18.19B |
| Short Term Debt | 19.13B | 13.13B | 12.5B | 13.21B | 13.19B |
| Current Portion of Long Term Debt | 3.55B | 2.68B | 3.53B | 3.3B | 5B |
| Accounts Payable | 2.09B | 2.8B | 2.68B | 2.29B | 2.5B |
| Income Tax Payable | 400M | 1.07B | 999M | 410M | 378M |
| Other Current Liabilities | 7.2B | 7.26B | 6.83B | 7.99B | 8.16B |
Dividends Payable |
– | – | – | – | – |
| Accrued Payroll | 997M | 936M | 857M | 854M | 894M |
| Miscellaneous Current Liabilities | 6.21B | 6.32B | 5.97B | 7.14B | 7.26B |
| Total Current Liabilities | 32.37B | 26.93B | 26.53B | 27.19B | 29.22B |
| Long-Term Debt | 19.06B | 28.31B | 29.68B | 31.18B | 25.36B |
| Long-Term Debt excl. Capitalized Leases | 19.06B | 28.31B | 29.68B | 31.18B | 25.36B |
| Non-Convertible Debt | 19.06B | 28.31B | 29.68B | 31.18B | 25.36B |
Convertible Debt |
– | – | – | – | – |
| Capitalized Lease Obligations | – | – | – | – | – |
| Provision for Risks & Charges | – | – | – | – | – |
| Deferred Taxes | 5.32B | 4.33B | 3.43B | 2.19B | (734M) |
| Deferred Taxes – Credit | 5.64B | 4.69B | 3.75B | 2.52B | 1.93B |
| Deferred Taxes – Debit | 319M | 360M | 326M | 330M | 2.67B |
| Other Liabilities | 4.39B | 4.3B | 4.08B | 8.02B | 7.64B |
| Other Liabilities (excl. Deferred Income) | 4.39B | 4.3B | 4.08B | 8.02B | 7.64B |
Deferred Income |
– | – | – | – | – |
| Total Liabilities | 61.46B | 64.23B | 64.05B | 68.92B | 64.16B |
| Non-Equity Reserves | – | – | – | – | – |
| Preferred Stock (Carrying Value) | – | – | – | – | – |
| Redeemable Preferred Stock | – | – | – | – | – |
| Non-Redeemable Preferred Stock | – | – | – | – | – |
| Common Equity (Total) | 30.32B | 25.55B | 23.06B | 17.07B | 16.98B |
| Common Stock Par/Carry Value | 1.76B | 1.76B | 1.76B | 1.76B | 1.76B |
| Retained Earnings | 63.41B | 65.02B | 65.5B | 60.43B | 63.23B |
| ESOP Debt Guarantee | – | – | – | – | – |
| Cumulative Translation Adjustment/Unrealized For. Exch. Gain | (5.23B) | (9.17B) | (9.78B) | (8.96B) | (11.05B) |
| Unrealized Gain/Loss Marketable Securities | 972M | 288M | 305M | 493M | 50M |
| Revaluation Reserves | – | – | – | – | – |
| Treasury Stock | (42.23B) | (45.07B) | (47.99B) | (50.68B) | (51.72B) |
| Total Shareholders’ Equity | 30.32B | 25.55B | 23.06B | 17.07B | 16.98B |
| Accumulated Minority Interest | 241M | 210M | 158M | 1.91B | 2.08B |
| Total Equity | 30.56B | 25.76B | 23.22B | 18.98B | 19.06B |
| Liabilities & Shareholders’ Equity | 92.02B | 90B | 87.27B | 87.9B | 83.22B |
B. Income statement GDP代写
| USD $ in millions | |||||
| 12 months ended | Dec 31, 2018 | Dec 31, 2017 | Dec 31, 2016 | Dec 31, 2015 | Dec 31, 2014 |
| Net operating revenues | 31,856 | 35,410 | 41,863 | 44,294 | 45,998 |
| Cost of goods sold | -11,770 | -13,256 | -16,465 | -17,482 | -17,889 |
| Gross profit | 20,086 | 22,154 | 25,398 | 26,812 | 28,109 |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | -10,307 | -12,496 | -15,262 | -16,427 | -17,218 |
| Other operating charges | -1,079 | -2,157 | -1,510 | -1,657 | -1,183 |
| Operating income | 8,700 | 7,501 | 8,626 | 8,728 | 9,708 |
| Interest income | 682 | 677 | 642 | 613 | 594 |
| Interest expense | -919 | -841 | -733 | -856 | -483 |
| Equity income, net | 1,008 | 1,071 | 835 | 489 | 769 |
| Other income (loss), net | -1,121 | -1,666 | -1,234 | 631 | -1,263 |
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 8,350 | 6,742 | 8,136 | 9,605 | 9,325 |
| Income taxes from continuing operations | -1,623 | -5,560 | -1,586 | -2,239 | -2,201 |
| Net income from continuing operations | 6,727 | 1,182 | 6,550 | 7,366 | 7,124 |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | -251 | 101 | – | – | – |
| Consolidated net income | 6,476 | 1,283 | 6,550 | 7,366 | 7,124 |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | -42 | -35 | -23 | -15 | -26 |
| Net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company | 6,434 | 1,248 | 6,527 | 7,351 | 7,098 |
2.2 GDP代写
| Fiscal year is January-December. All values USD millions. | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Cash Only | 8.96B | 7.31B | 8.56B | 6.01B | 8.93B |
| Total Accounts Receivable | 4.47B | 3.94B | 3.86B | 3.67B | 3.4B |
| Accounts Receivables, Gross | 4.8B | 4.29B | 4.32B | 4.14B | 3.89B |
| Inventories | 3.1B | 2.9B | 2.68B | 2.66B | 2.77B |
| Total Current Assets | 32.99B | 33.4B | 34.01B | 36.55B | 30.63B |
| Net Property, Plant & Equipment | 14.63B | 12.57B | 10.64B | 8.2B | 8.23B |
| Total Assets | 92.02B | 90B | 87.27B | 87.9B | 83.22B |
| Total Current Liabilities | 32.37B | 26.93B | 26.53B | 27.19B | 29.22B |
| Long-Term Debt | 19.06B | 28.31B | 29.68B | 31.18B | 25.36B |
| Long-Term Debt excl. Capitalized Leases | 19.06B | 28.31B | 29.68B | 31.18B | 25.36B |
| Non-Convertible Debt | 19.06B | 28.31B | 29.68B | 31.18B | 25.36B |
| Total Liabilities | 61.46B | 64.23B | 64.05B | 68.92B | 64.16B |
| Total Equity | 30.56B | 25.76B | 23.22B | 18.98B | 19.06B |
| quick ratio | 92% | 113% | 118% | 125% | 95% |
2.3 GDP代写
Coca-Cola reports its net revenue in two segments: concentrate operations and finished product operations. Coca-Cola manufactures and sells syrup to authorized bottlers to make finished Coca-Cola products and manufacture fountain syrups. This revenue is reported under the company’s concentrate operations. The company also manufactures its own fountain syrups, manages several bottling operations, and collects revenue on finished products.
2.4
The analyse of Balance sheet
| Assets | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| Cash Only | 9.74% | 8.12% | 9.81% | 6.84% | 10.73% |
| Accounts Receivales, Gross | 5.22% | 4.77% | 4.95% | 4.71% | 4.67% |
| Inventories | 3.37% | 3.22% | 3.07% | 3.03% | 3.33% |
| Other Current Assets | 4.08% | 7.39% | 6.05% | 10.86% | 10.23% |
| Total Current Assets | 35.85% | 37.11% | 38.97% | 41.58% | 36.81% |
| Property, Plant & Equipment – Gross | 27.45% | 24.83% | 24.36% | 18.71% | 19.53% |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 11.55% | 10.87% | 12.17% | 9.39% | 9.63% |
| Net Goodwill | 13.15% | 12.54% | 12.18% | 10.69% | 12.33% |
| Other Assets | 3.28% | 3.03% | 3.11% | 3.07% | 3.28% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Short Term Det | 20.79% | 14.59% | 14.32% | 15.03% | 15.85% |
| Accounts Payale | 2.27% | 3.11% | 3.07% | 2.61% | 3.00% |
| Income Tax Payale | 0.43% | 1.19% | 1.14% | 0.47% | 0.45% |
| Accrued Payroll | 1.08% | 1.04% | 0.98% | 0.97% | 1.07% |
| Total Current Liailities | 35.18% | 29.93% | 30.40% | 30.93% | 35.11% |
| Long-Term Det | 20.71% | 31.46% | 34.01% | 35.47% | 30.47% |
| Deferred Taxes | 5.78% | 4.81% | 3.93% | 2.49% | -0.88% |
| Other Liailities | 4.77% | 4.78% | 4.68% | 9.12% | 9.18% |
| Total Liailities | 66.79% | 71.37% | 73.39% | 78.41% | 77.10% |
| Common Equity (Total) | 32.95% | 28.39% | 26.42% | 19.42% | 20.40% |
| Retained Earnings | 68.91% | 72.25% | 75.05% | 68.75% | 75.98% |
| Treasury Stock | -45.89% | -50.08% | -54.99% | -57.66% | -62.15% |
| Total Equity | 33.21% | 28.63% | 26.61% | 21.59% | 22.90% |
| Total Liabilities & Equity | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
The analyse of Income statement GDP代写
| 12 months ended | Dec 31, 2018 | Dec 31, 2017 | Dec 31, 2016 | Dec 31, 2015 | Dec 31, 2014 |
| Net operating revenues | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Cost of goods sold | -36.95% | -37.44% | -39.33% | -39.47% | -38.89% |
| Gross profit | 63.05% | 62.56% | 60.67% | 60.53% | 61.11% |
| Selling, general and administrative expenses | -32.35% | -35.29% | -36.46% | -37.09% | -37.43% |
| Other operating charges | -3.39% | -6.09% | -3.61% | -3.74% | -2.57% |
| Operating income | 27.31% | 21.18% | 20.61% | 19.70% | 21.11% |
| Interest income | 2.14% | 1.91% | 1.53% | 1.38% | 1.29% |
| Interest expense | -2.88% | -2.38% | -1.75% | -1.93% | -1.05% |
| Equity income, net | 3.16% | 3.02% | 1.99% | 1.10% | 1.67% |
| Other income (loss), net | -3.52% | -4.70% | -2.95% | 1.42% | -2.75% |
| Income from continuing operations before income taxes | 26.21% | 19.04% | 19.43% | 21.68% | 20.27% |
| Income taxes from continuing operations | -5.09% | -15.70% | -3.79% | -5.05% | -4.78% |
| Net income from continuing operations | 21.12% | 3.34% | 15.65% | 16.63% | 15.49% |
| Income (loss) from discontinued operations, net of income taxes | -0.79% | 0.29% | |||
| Consolidated net income | 20.33% | 3.62% | 15.65% | 16.63% | 15.49% |
| Net income attributable to noncontrolling interests | -0.13% | -0.10% | -0.05% | -0.03% | -0.06% |
| Net income attributable to shareowners of The Coca-Cola Company | 20.20% | 3.52% | 15.59% | 16.60% | 15.43% |
2.5 Pepsi and Red Bull GDP代写
Pepsi – Coca-Cola’s largest and closest competitor; its main competitor, the brand covers multiple categories, including herbal drinks, health and energy drinks, and bottled water and juice. In fact, Pepsi is the toughest competitor of Coca-Cola, and their competition has been called the Coke War.
Red Bull – Red Bull has a limited product portfolio but is a major competitor to Coca-Cola’s energy drink products. Red Bull is Coca-Cola’s most powerful energy drink competitor.
2.6
The Profitability Score is a relevant measure for the assessment of a stock attractiveness. The Coca-Cola Company shows a Profitability Score of 9.00.
The Profitability Score for The Coca-Cola Company is significantly higher than its peer group’s. This means that The Coca-Cola Company has a significantly higher profitability than its peer group.
2.7 GDP代写
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 |
| 168.7B | 179.9B | 192.8B | 182.9B | 206.8B |
I would not recommend Coca-Cola’s stock. The Coca-Cola Company has had little success in achieving multi-business in the past few years compared to its competitors. Its business growth is not only slow but also heavily dependent on the single pillar of beverages.
3.1
| BALANCE SHEET | |
| Assets | |
| Cash | 38,000 |
| Account Receivable | 60,000 |
| Inventories | 15,600 |
| Total Current Assets | 113,600 |
| Building at acquisition cost | 120,000 |
| Building accumulated depreciation, as at 31. 12. 2X14 | 30000 |
| Transport vehicles at acquisition cost | 200,000 |
| Transport vehicles accumulated depreciation, as at 31. 12. | 88000 |
| Net Fixed Assets | 320,000 |
| Total Assets | 433,600 |
| Liabilities and Equity | |
| Current portion of LTD | 9000 |
| Account payables | 45400 |
| Accruals | 3600 |
| Revolving Bank Credit | |
| Total Current Liabilities | 58000 |
| Long-Term Debt (Mortgage) | 27,000 |
| Total Liabilities | 85,000 |
| Equity | 125000 |
| Retained earnings | 223600 |
| Total Equity | 348600 |
| Total Liabilities and Equity | 433,600 |
更多其他:Essay代写 研究论文代写 期末论文代写 毕业论文代写 论文代写 prensentation代写 Resume代写 Report代写 Proposal代写



您必须登录才能发表评论。