AGILE AND TRADITIONAL PROJECT MANAGEMENT
By
Course
Instructor
Institution
Location
Date
Agile and Traditional代写 In recent years, Agile project management has become popular with many software developers because of its efficiency.
Agile and Traditional Project Management Agile and Traditional代写
In recent years, Agile project management has become popular with many software developers because of its efficiency. It has become an essential pillar that businesses and teams use to run effectively and efficiently. Few companies have adopted the use of agile methodology and due to the rigidity in organizational culture. Traditional project management methodology is suitable in specific projects but mainly used in less complicated projects. Between agile and traditional approaches, agile is considered the most practical and flexible software development that is preferred over traditional methodology.
Issues with the traditional approach to project management Agile and Traditional代写
Traditional approach is linear, where all phases of the process follow a sequence of events (Koi-Akrofi, Koi-Akrofi, and Matey, 2019, p. 35). The approach uses predictable tools and experience. All projects follow a predetermined workflow cycle with stages flowing from feasibility, plan, design, test, production, and support, as shown in figure 1 below. As such, the whole project is planned before the actual development process without room for adjustments in future. The traditional method assumes that time and costs are variable in both short-run and long-run and that project specification is fixed.Agile and Traditional代写**格式
According to Koi-Akrofi, Koi-Akrofi, and Matey, (2019, p. 38), there are challenges and disadvantages associated with the traditional approach that makes agile method most preferred project management. The conventional approach is monolithic and slow, especially when the client is not sure or clear about the project requirements. Inflexible nature of the method makes changes difficult.Agile and Traditional代写**格式
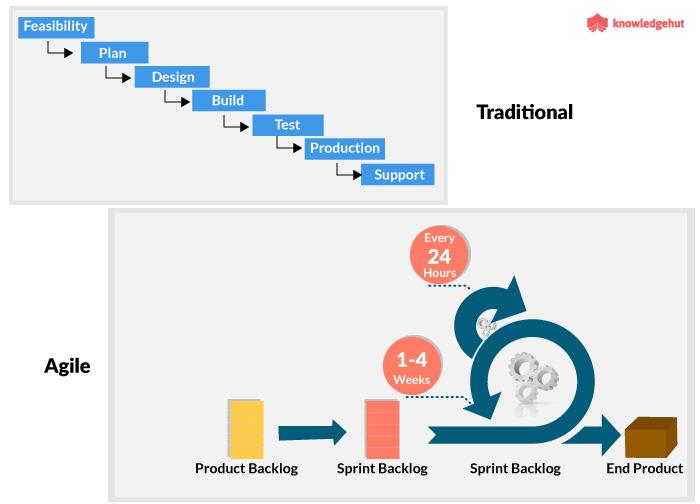
Figure 1: Workflow for traditional and agile project management methods.
Source: Rongala (2019) Agile and Traditional代写
The traditional approach has no customer focal point.
Since the process is linear and static, there is not much space for the input from a client in all steps of the project except at the commencement stage (Koi-Akrofi, Koi-Akrofi, and Matey, 2019, p. 36). The team does not involve the client or the project does not allow a room for client involvement until the project is delivered. Therefore, if there was a misrepresentation or missing information on the client’s requirement, then the whole project may be a time-wasting phenomenon. When the product is finalized, it might be too late to cross-check it with client requirement. Customer satisfaction is a priority because it determines the position of the software developer in the market.
Additionally, the classical approach follows a strict chain of command, lacks proper time management, and lack intuitiveness (Koi-Akrofi, Koi-Akrofi, and Matey, 2019, p. 36). Agile and Traditional代写
The project has an individual subcontracted to control a rope of development. It also lacks singular teamwork and leadership as a central authority. Also, the lack of cooperation, unity, and shared development cause mismanagement of time in this approach. Besides, the fact that the project is predetermined before inception, little room is left for new ideas in traditional methodology. The sequence of events limits client or persona inputs and hence lacks the opportunity for continuous evolution.
Moreover, the traditional method is rigid and resistant to change. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
A software that has already been developed and is at the testing stage becomes difficult and expensive, or impossible to backtrack the processes to track or fix problems according to the client requirements (Koi-Akrofi, Koi-Akrofi, and Matey, 2019, p. 37). Due to this rigidity, the development team end up starting afresh to make changes in the software. Therefore, risk involving and challenging development. The reason being sometimes, clients are not sure of the software requirement at the beginning of the project, and hence it cannot start before all the relevant details and specifications are gathered. Also, the traditional method offers limited client involvement for feedback. Therefore, it is not an excellent model to develop complex, broad, and object-oriented project development.
Agile approach Agile and Traditional代写
Lansing, Kishnah and Pudaruth (2012) stated that agile project management is a concept for software development where teams work on various parts of the software in iteration and in a span of time. According to Agile Manifesto, the agile method is based on principles, allow iteration and incremental implementation, corporation and team and stakeholder integration and self-organization and frequent and constant reviews (Sheffield, and Lemétayer, 2013, p. 459). Iteration and incremental approach aim to release benefits throughout the process rather than only at the end.
Agile project management is vested in four central values that developers follow (Schön, Escalona, and Thomaschewski, 2015, 62). Agile and Traditional代写**格式
First, the method value individual and interactions rather than process and tools. The team focus on building the capacity of each individual through skills, cooperation and collaboration that ensure faster delivery of the product. The development does not focus on the process and tools like the case of a traditional approach. Secondly, the approach does not value elaborate documentation of the software but focus on working software.
Thirdly, agile focuses on client involvement over contract negotiation. The team work together with the client to get regular reviews and changes for improvement to deliver quality software and create customer satisfaction. Lastly, agile development has to be flexible rather than strictly adhering to the project plan, so that client inputs to the project are put into consideration. These values guide the agile team throughout the process of development.
Additionally, there are 12 principles outlined in the Agile Manifesto (Juricek, 2014, 172). Agile and Traditional代写
First, customer satisfaction and time of delivery are paramount in agile development. As such, the teamwork offers continuous delivery of valuable parts of work completed mainly to get client review. Secondly, the project is subdivided into smaller independent tasks to allow ongoing deliveries and inspections. Thirdly, agile management is made of small, self-organized teams, and members feel responsible for overall project success.
Each member of the team works to protect the integrity of the whole groups because the failure of one means the failure of the entire team. Also, the failure of one group does not mean the failure of the entire project team but the link. Therefore, members of the teamwork together in collaboration to share in the success of the entire project. Fourth, agile provides a motivating and supportive environment for individuals and trust them to complete the jobs assigned with little control. Trust is the key where leaders believe in their team and teams are committed to delivering their roles.
Fifth, the team has to establish a common ground for sustainable efforts to the end of the project. Agile and Traditional代写
All team members must agree on the rules governing the project so that they can own them and take responsibility. Sixth, being consistent with time and delivery. The jobs should be completed within a stipulated time. Seventh, client input is allowed at all levels of development. Thus, the client is an integral part of all stages to ensure continuous review and improvement of the project before final delivery. Eighth, regular meeting with the client and team is necessary to iron out the challenges and problems facing the project. Constant monitoring ensures the project is delivered on time and within the cost estimate.
Nineth, regular reflection on the progress made, challenges and adjustments necessary to provide quality work. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
Team reflection ensures identification of inefficiencies and correction measures taken. Tenth, the progress of the project is measured by the completed part to ensuring planning and fast-tracking uncompleted work. Eleventh, the team should strive to provide the best product to their best capacity, resources and requirement by the client and not be satisfied for excellence. Lastly, agile development is dynamic and adaptive to changes to attain project and the firm a competitive advantage in the industry. These principles constitute the fundamental pillars on which agile project management is built.
On the other hand, agile proposes an incremental and iterative approach in software development. Agile and Traditional代写
Like there are many types of projects, there are also various types of agile methodologies including Scrum, extreme project management, adaptive project management and dynamic method of project management, among others. Scrum is frequently used and a perfect reflection of a general agile approach. As such, Scrum methodology is used to gain a better understanding of how an agile process works. In Scrum methods, the master is the epicenter of roles. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
A Scrum Master has the role of mediating between the team and the client and reliable information that ensure the project is in sync with the client specifications. Below is figure 2 illustrating the lifecycle process in agile methodology.
At the beginning of the project, the client divided the project requirements into user stories. Agile and Traditional代写
The Scrum master take the user stories and come up with different sprints. Each sprint contains 3-4 user stories that are deliverable within 4 to 5 weeks but which can change depending on the project complexity. When the sprint planning is complete, the user stories are further divided into tasks that give the developer the roadmap of the whole project. The client review, and propose changes the project at the end of each sprint.
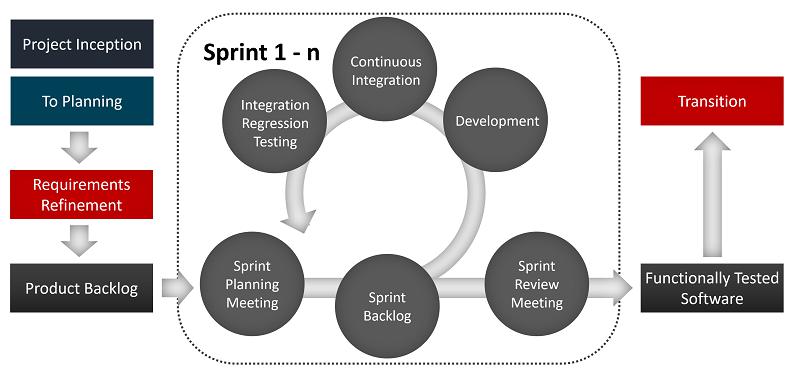
Figure 2: Lifecycle process in agile methodology
Source: Mavuru (2018) Agile and Traditional代写
Differences between agile and traditional methods
The main difference between agile and traditional project management is the sequence of events, as shown in figure 1. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
The traditional approach uses linear sequence while the agile approach uses iterative. Besides, the differences between the two are discussed by various authors. Hoda, Noble, and Marshall (2008, p. 218) noted that the differences between the two are found in the development lifecycle. In a real sense, I.T. development lifecycle is dynamic and hence request frequent reviews and changes regarding client specifications.
The agile method becomes the most suitable because it allows for client reviews and inputs through the project lifecycle, unlike the traditional method that is linear and does not allow changes in the progress. Since the traditional method is linear, the lower phase has to be complete to continue with the higher phase. Thus, after the client has given all the requirements and the project has commenced, it will be difficult to make changes in requirements in future. The agile method solves this problem by allowing flexibility through customer involvement, constant reviews and controls and implementation of changes.
Additionally, Stare (2014, p. 296) outlined four main differences between traditional and agile approach. Agile and Traditional代写
Including requirement and specification, project scheduling, team, and customer involvement. Agile does not rely on the team alone to prepare the requirements of the project. It involves the client to gather the project specification at all iterations (Brandon, 2006). Client role in the project includes evaluation of functions and suggestion of changes. The collaboration ensures that less important features are eliminated at the planning stages or beginning of each iteration. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
However, in the traditional method, almost everything mentioned above in agile is the opposite. The project manager and the team prepare the requirements and the extent of client collaboration is less compared to agile. The requirements are not defined in iteration but before the beginning of the whole project. Thus, after the requirements are accepted, and the project commences, it becomes difficult to make changes unless critical elements are missing. Project requirements are defined right from start to end of the project.
Furthermore, the traditional method uses project planning tools such as Gantt chart, Microsoft project and critical path method. Agile and Traditional代写
The whole project is broken down into activities as they should follow each other without overlapping. The overlapping is avoided because of dependencies that exist in each step. Agile, on the other hand, use short iterations that are not more than eight weeks. The scheduling is done at the beginning of the project and the start of each iteration. The team is self-organized, and trust exists in execution, assignments and roles. Tests and reviews, as well as implementation of changes, are done at the beginning of each iteration.
Moreover, the traditional method development team is not dynamic, and the project manager is the CEO of the project team.
There are other heads such as technical lead, changes management, human resource affairs, among others. The project manager reports to the program manager and the program manager report to the steering committee. The chain of command also reflects the level of authority in issue resolutions. Unlike the traditional method, the agile approach has a self-organized and accountable to deliver the project as per the client specifications, propose changes, and solve problems. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
The decisions are made in teams and regular meetings. The method allows for individuals to learn from their mistakes and others, make necessary changes, and plan for future improvements. Overall, the agile methodology allows transparency because the client and the team members collaborate in decision-making. Whereas, traditional method, the project manager holds reins of the project and the team members have no role in making major decisions (Kashyap, 2018). The agile methodology, therefore, facilitates team members to see the project progress from start to the end.

Importance of agile for project success Agile and Traditional代写
There is four main importance of agile that contribute to project success. First, the approach offers the efficiency of the project. The teams work in a collaborative culture where each member is responsible for the success of the project. The teams make collective agreements on target and ground rules and each member identify with them. The teams are characterized by the interconnectedness of relationships in accomplishing tasks. As such, the whole team move in unison, on iteration, towards achieving quality project at the end. Secondly, the approach targets to deliver beyond excellence.
Tests are done at all stages of the development cycle to ensure the product is delivered at the required quality, and implement changes. High quality is maintained by continuously involving the client to review and suggest changes. Thirdly, the agile method increases the predictability of the project. The team and the owner can value the project on the grounds of cost and returns on investment. If ROI is higher than cost, then the project is viable and vice versa. Lastly, the method ensures the adaptability of a software development team. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
Flexibility in teams is exhibited through client involvement and evaluations and need for implementation of suggested changes. The ability to adjust the project to client needs is a cornerstone for a successful project.
Reflection Agile and Traditional代写
Need for both traditional and agile methods
Although it is tempting for one to assume that the agile method is best for all projects, it is not true. While the agile approach can be used for any project for its powerful benefits, there are instances where the traditional method is a better way to project development. For instance, the traditional method is used in an enterprise with a standardized process. Thus, most projects are not entirely agile or traditionally managed. Agile and Traditional代写**格式
Some project benefits most when a blend of both methods is used to utilize their strengths and complementing each other’s weaknesses (Conforto, and Amaral, 2016, p. 7). Agile, on the one hand, allows for iteration and frequent release of project for client review and suggestions. The traditional approach, on the other hand, reduces project errors and their severity. Additionally, a successful project is a combination of good planning and Q.A. input in the early development process to reduce the rate of errors while the introduction of the agile method in the release schedule and allow user feedback enhance faster development and project improvements.
Role and impact of project management Agile and Traditional代写
Project management is a holistic approach to ensuring the project begins and delivered successful (Machado, and Martes, 2015, p. 29). It involves planning, initiating, executing, monitoring and control and providing the project. The project management ensures the team works on common ground and towards a goal of delivering a project that meets the need of the client. Agile method is a modern approach to project management and came to reduce the weaknesses in the traditional approach.
The agile process allows collaboration of stakeholders and the dynamics of project development to play (Fageha, and Aibinu, 2013, p. 159). As such, it solves common problems that were occurring when using the traditional method. Nonetheless, a hybrid approach of the two can be used to increase productivity. Overall, effective project management should deliver a high-quality project within the timeline and cost.

References Agile and Traditional代写
A
Aljaž, S., 2014. Agile Project Management in Product Development Projects. ScienceDirect. Elsevier. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences 119, pp. 295-304.
Agile Manifesto. The Agile Manifesto, [Online]. Available: www.Agilemanifesto.org. [Accessed on 20 April 2020)
B
Brandon, D., 2006. Project management for modern information systems. Hershey: IRM Press.
C
Conforto, E.C. and Amaral, D.C., 2016. Agile project management and stage-gate model—A hybrid framework for technology-based companies. Journal of Engineering and Technology Management, 40, pp.1-14.
F
Fageha, M.K. and Aibinu, A.A., 2013. Managing project scope definition to improve stakeholders’ participation and enhance project outcome. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 74(29), pp.154-164.
H
Hoda, R., Noble, J and Marshall, S. 2008. Agile Project Management. In J. Holland, A. Nicholas, &D. Brignoli (Eds.), New Zealand Computer Science Research Student Conference, NZCSRSC 2008 – Proceedings (pp. 218-221). Christchurch, New Zealand. Retrieved from https://nzcsrsc08.canterbury.ac.nz/site/proceedings/NZCSRSC_2008_Proceedings.pdf
J
Juricek, J., 2014. Agile project management principles. Lecture Notes on Software Engineering, 2(2), p.172.
K
Koi-Akrofi, G. T, Koi-Akrofi, J & Matey, H.A., 2019. Understanding The Characteristics, Benefits And Challenges Of Agile I.T. Project Management: A Literature-Based Perspective. International Journal of Software Engineering & Applications, 10(5), pp. 25-44, DOI: 10.5121/ijsea.2019.10502
Kashyap, S., 2018. Traditional vs Agile Project Management Method: Which One is Right for Your Project? Available from https://www.proofhub.com/articles/traditional-vs-agile-project-management (Accessed on 21 April 2020)
M
Machado, F. and Martes, C.D., 2015. Project management success: a bibliometric analysis. Revista de Gestão e Projetos-GeP, 6(1), pp.28-44.
Mavuru, I. 2018. Traditional vs Agile Software Development Methodologies. KPI Partners. Available from http://www.kpipartners.com/blog/traditional-vs-agile-software-development-methodologies (Accessed on 21 April 2020)
R
Rongala, A. 2019. Know Your PMP Methodology From Your Scrum. Invensis. Available from https://www.invensislearning.com/blog/project-management-methodologies/ (Accessed on 21 April 2020)
S
Sheffield, J. and Lemétayer, J., 2013. Factors associated with the software development agility of successful projects. International Journal of Project Management, 31(3), pp.459-472.
Schön, E.M., Escalona, M.J. and Thomaschewski, J., 2015. Agile values and their implementation in practice. IJIMAI, 3(5), pp.61-66.
V
Vikash, L, Somveer, K and Sameerchand, P. 2012. People factors in agile software development and project management. International Journal of Software Engineering & Applications (IJSEA), 3(1)
更多其他:Case study代写 心理学论文代写 毕业论文代写 论文代写 Essay代写 研究论文代写 论文代写 Academic代写 Review代写 网课代修 代写CS Essay代写 数据分析代写 润色修改 代写案例




您必须登录才能发表评论。