Financial Analysis
公司财务代写 Apogee company, Inc. is a company located in the US. It was initially known as the Arch of Illinois company.
APOGEE COAL COMPANY ANALYSIS
Apogee company, Inc. is a company located in the US. It was initially known as the Arch of Illinois company. The company has it headquarter in the United States, and was a subsidiary of the Magnum company coal. From January in the year 2009, the company started to operate as the subsidiary of Patriot coal corporations. Since the establishment of the Apogee company, many operations have been carried out that have impacted its stability. The company has gone further in ensuring that they perform best to attain the set goals and key objectives. The company has an excellent performance record in ensuring that it maintains its stability in providing products in its service line.
Apogee company is widely known for delivering innovative services and products and doing so in such a way that helps conserve its resources. The company provides architectural products and services that help achieve the architects, the buildings’ development, and the owner’s ideal designs, commonly referred to as a green building. These green buildings play a part in achieving the company’s sustainable goals
The company has an extension of comprehensive line-ups that substitute it in the industry. This initiative has to lead to the production of products and services by a company that is driven through research and promotes new products’ creation and development. The company has strived to improve in most business activities. It has effectuated this process by ensuring it provides high-quality services and products.
2.Financial Analysis 公司财务代写
Observations
The financial statement’s observation shows that the Apogee Company’s financial performance keeps on rising each year. For instance, the balance sheet showed an improvement in the Net Cash amount from 1068168 in 2019 to 1128991 in 2020. The results from this record show quite a significant improvement. From the income statement, there is a decline in the Net Income from 57784 in 2019 to 577889 in 2018. The company then recorded a substantial rise in 2020 to 61914.
3.Ratio Analysis
i) Liquidity Ratio – A liquidity ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay off short-term debt burdens, not excluding the quick ratios, current ratios, and cash flow ratios used to calculate the margin of safety.
They include the ratios below.
| a) Current ratio | |||
| Current Asset/ Current Liability | |||
| 2019 | 2020 | ||
| 371898/272512 | 381910/276857 | ||
| 1.36 | 1.38 | ||
| 1.36:1 | 1.37:1 | ||
| b) Quick ratio | |||
| (Current Asset- inventory)/ Current Liability 公司财务代写 | |||
| 2019 | 2020 | ||
| (371898-78344-16451)/272512 | (381910-71089-25481)/276857 | ||
| 1.02 | 1.03 | ||
| c) Cash ratio | |||
| (Cash + Marketable security)/Current Liability | |||
| 2019 | 2020 | ||
| 17087/272512 | 14952/276857 | ||
| 0.06 | 0.05 | ||
| d) Working Capital ratio | |||
| Current Assets-Current Liability | |||
| 2019 | 2020 | ||
| 371898-272512 | 381910-276857 | ||
| 99386 | 105053 | ||
From the liquidity ratio computed above, it can be noted that the company is in a position to pay off its short-term liabilities, which would otherwise impact negatively on the company as it keeps increasing over the years (FROST, 2009). From the above ratios, it can also be noted that the company has enough solid cash to sustain its operational activities. From the above computations, it can also be noted that in 2019, the working capital was 99386 and increased to 105053 in 2020. These results show that the company is in an excellent financial position to cater to its short-term obligations and finance other small activities that come along in the organization. The current ratio value shows how much of the company’s assets can be easily converted into cash and was 1.36 in the year 2019 compared to 1.37 the following year, showing an increment by 0.01 units.
ii) Solvency Ratio –This is a crucial ratio and is used to determine the company’s ability to pay off its long-term debt obligations and can be used to measure the financial state of a company. 公司财务代写
It includes the following ratios:
| a) Debt ratio | |
| Total debts/ Total assets | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 245724/1068168 | 212500/1128991 |
| 0.23 | 0.19 |
| b) Debt to equity ratio | |
| Liabilities/Equity | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 550418/496317 | 612213/516778 |
| 1.11 | 1.18 |
| c) Equity Multiplier ratio | |
| Assets / Equity | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 10681868/496317 | 1128991/516778 |
| 2.15 | 2.18 |
The company uses these ratios to determine the financial state of the organization. According to the percentages above, the company is in a good financial position. It has enough cash to repay its long-term debts, acquired in financing its investments and projects (Liao & Chen, 2005). At this point, we can say that the company is highly leveraged. Under this case, considering the equity multiplier ratio, it can be noted that the balance is at 2.15 in 2019 and stands at 2.18 in 2020, which clearly shows that the company is operating in its standards. When a company reaches such a state, it can carry out most of its business operations and simultaneously facilitate the company’s growth and expansion.
iii) Capability to pay interest. This ratio includes; 公司财务代写
| a) Time-interest earned ratio | |
| EBIT/ interest expense | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 67284/58662 | 87848/79750 |
| 1.15 | 1.10 |
| b) Cash coverage ratio | |
| Cash and Equivalent/ Current Liabilities | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 17087/227512 | 14952/276857 |
| 0.08 | 0.05 |
The ratios on interest are more like the coverage ratios and are used in determining the number of times a company can acquire a current claim by utilizing its available earnings. (“Issue Information,” 2018). In some cases, it can be noted that the interest ratio measures the company’s ability to pay the interests on its debts over a certain period of time. In these cases, the coverage interest period ratio is used to determine the company’s easiest way to pay off its outstanding debts and interest expenses.
iv) Asset management ratio– 公司财务代写
| a) Inventory turnover | b) Day’s sale in inventory | |||||||
| COGS/ Average turnover | 365/ Inventory turnover | |||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||
| 1109072/192767 | 1068480/194786.5 | 365/5.75 | 365/5.49 | |||||
| 5.75 | 5.49 | 63.48 | 66.48 | |||||
| 5.75 times | 5.49 times | 63.48 days | 66.48 days | |||||
| c) Receivable Turnover | d) Day’s sales outstanding | |||||||
| Credit sales/ Average Receivables | 365/ receivables turnover | |||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||
| 1402637/72219 | 1387439/70637.5 | 365/19.42 | 365/19.64 | |||||
| 19.42 | 19.64 | 18.80 | 18.58 | |||||
| 19.42 times | 19.64 times | 18.80 days | 18.58 days | |||||
|
|
|
|||||||
| e) Total assets turnover | f) Fixed asset turnover | |||||||
| Net sales/ Average Assets | Net sales/ Fixed assets | |||||||
| 2019 | 2020 | 2019 | 2020 | |||||
| 1402637/1068168 | 1387439/1128991 | 1402637/315823 | 1387439/324386 | |||||
| 1.31 | 1.23 | 4.44 | 4.28 | |||||
| 1.31 times | 1.23 times | 4.44 times | 4.28 times | |||||
Assets management is a ratio that determines the amount of inventory that a company can invest in to facilitate more income. This percentage is essential as inventory is the current asset that helps a company manage its short-term obligations. Another aspect to consider is the receivable turnover, where the company looks at the number of days for collecting the debts from the debtors (FROST, 2009). In our case, when there are shorter days, it’s said that the company has a suitable mechanism for the debt collection period.
v) Profitability ratio. The below ratios are the company’s way of generating the net profit for the shareholders.
| a) Profit Margin | |
| (sales -COGS)/ Net sale | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| (1402637-1109072)/1402637 | (1387439-1068480)/1387439 |
| 0.21 | 0.23 |
| 21% | 23% |
| b) ROA (Return on Asset) | |
| Operating income / Total Assets | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 67284/1068168 | 87848/1128991 |
| 0.06 | 0.08 |
| 6% | 8% |
| c) ROE (Return on Equity) | |
| Net Income/ Shareholder’s Equity | |
| 2019 | 2020 |
| 67284/496317 | 87848/516778 |
| 0.14 | 0.17 |
| 14% | 17% |
A company stands in a better position if its profits can pay back dividends to all its shareholders. This initiative enables a company to deploy a good image to the investors. The return on equity shows how the company has utilized the shareholder’s funds and its position to generate more profit and income. In the year 2019, the company had a 14% ROE which improved to 17% in 2020, showing an improvement of 3%. 公司财务代写
This improvement is impressive and shows that the company is also improving in its long run. The ROA shows how the company uses its current assets to generate more income for company. (FROST, 2009). When the company reaches this stage, it implies that it has fully utilized its investments and generates the utmost income. In our case, the company has progressed from 6% to 8%, which is an improvement, showing how effectively the company has utilized its assets.
vi) Market value ratio – The ratio displays the company’s strength in the market by their investors.
| a) Price Earning ratio | ||||
| Price per share/ Earnings per share | EPS=net income/ no. of outstanding | |||
| 2019 | 2020 | 67284/27015 | 87848/26443 | |
| 18.37/2.49 | 19.54/3.32 | 2.49 | 3.32 | |
| 7.38 | 5.89 | |||
| b) Market to book ratio | ||||
| Market capitalization/Book value | ||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||
| 742041/315823 | 729278/324386 | |||
| 2.35 | 2.25 | |||
| c) EBITDA ratio | ||||
| Enterprise value/ EBITDA | ||||
| 2019 | 2020 | |||
| 1296805/67284 | 1326539/87848 | |||
| 19.27 | 15.10 | |||
b) From the above ratios, one can observe that the company effectively utilizes its assets and the shareholder’s equity in generating more income, as shown from the significant improvement in the company’s performance. This assessment indicates that the company is doing well and is generating more revenue (Anderson & Brooks, 2006). The profitability ratio shows how the company works.
c) From the observation, it can be noted that the number of days for the collection period should be reviewed, and proper adjustments made to make the days shorter. The credit policy terms should also be examined in order to improve credit terms. This ratio shows how many times the company uses an asset in the generation of income, which can help determine the amounts of debts to be collected and the collected amount (Anderson & Brooks, 2006). This ratio measures the company’s efficiency level in using its assets. The balance tries to elaborate on how easy the company can confirm the purchases into income, explaining why the company is doing well in the marketplace.
d) From the above computations, the ROE has changed. It has established that the company well utilizes the shareholder’s equity in establishing more profits and ensuring better performance in the company. The ROE has increased from 14% to 17%, indicating that the company has well utilized the shareholders’ equity.
Growth rate Model 公司财务代写
4.
| The growth rate in sale | (Current year- pervious)/Previous |
| (1387439-1402637)/1402637 | |
| -0.01 |
5
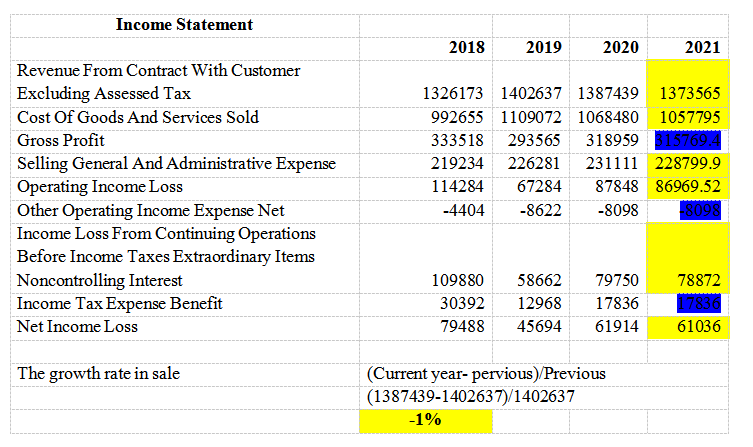
| Dividend’s payout ratio | dividends paid/ net income | |
| 2019 | 2020 | |
| 17864/45694 | 18714/61914 | |
| 0.39 | 0.30 | |
| 39% | 30% | |
| In 2021 (50%) | 18714/61036 | |
| 0.31 | ||
| 31% | ||
Assumptions.
i.The first assumption is that when the company pays 100% of the dividends, there is an equal amount of revenue used; therefore, the company would not have any amount to save.
ii.When the amount of money is paid out as dividends, it also reduces the retained amount of money.
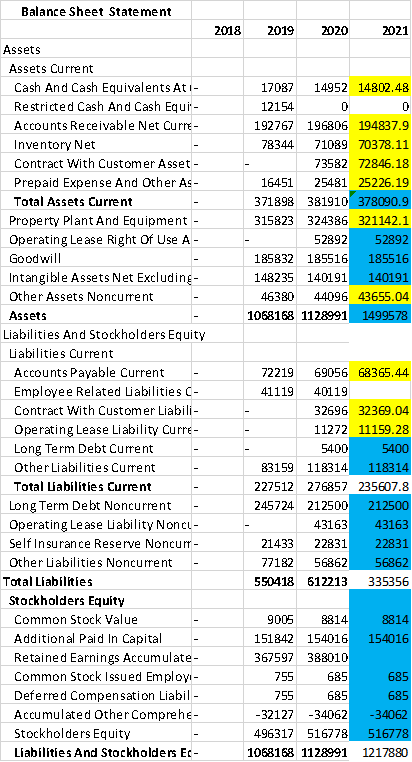
Calculation of EFN

= {1128991/1387439} *15198 – {612213/1387439} *15198- (0.13*1373565) * (1-0.3)
= -12367 – (-6706) -124994
= -130655
Conclusion 公司财务代写
In conclusion, it can be noted that the management and the department heads play a significant role in ensuring that a company performs well in its markets and has a good record in its different levels of operations. This initiative results from standards they set across, determining the revenue that an organization is likely to yield. When the proper measures are put in place, the anticipated performance in terms of gains and dividends is expected to be desirable. Managers and directors also help in the capitalization of the markets prompting the company to perform better. To determine the best performing company in the market, computations such as the earning per share, the dividend spent, and the payout ratios are used. Ratio analysis is an important tool as they help understand the organization’s financial trends and predict its performance.
Apart from the capitalization ratios, other essential ratios are also considered, such as the liquidity and solvency ratios.These ratios are also preferred as they evaluate the firm and show its financial position. Ratios also help the management to understand the economic trends in their company’s better. Directors use these percentages to assess the strengths and weaknesses from which initiatives are taken to make the required resolutions. These ratios are essential in evaluating and analyzing the trends in the financial state of an organization. Potential investors should also look into ratios such as the working capital, the debt-to-equity ratios, and the company’s asset management ratios before deciding to invest. Therefore, these ratios are helpful to both the management while implementing different strategies and help investors decide whether to buy or sell their stocks.
References 公司财务代写
AKYÜZ, İ. (2019). Future projection and the sales of industrial wood in Turkey: artificial neural networks. TURKISH JOURNAL of AGRICULTURE and FORESTRY, 43(3), 368–377. https://doi.org/10.3906/tar-1901-20
Anderson, K., & Brooks, C. (2006). Decomposing the price-earnings ratio. Journal of Asset Management, 6(6), 456–469. https://doi.org/10.1057/palgrave.jam.2240195
FROST, R. (2009). THE 30 PERCENT LIQUIDITY RATIO. Bulletin of the Oxford University Institute of Economics & Statistics, 15(1), 25–30. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-0084.1953.mp15001002.x
Issue Information. (2018). Ratio, 31(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/rati.12196
Leal, R., Nail, L., & Parisi, F. (2001). Introduction to the Latin American Financial Markets Special Issues of the International Review of Financial Analysis. International Review of Financial Analysis, 10(3), 201. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1057-5219(01)00049-7
Liao, H.-H., & Chen, T.-K. (2005). A Cyclicality Linked Corporate Short-term Credit Model – Solvency Ratio Approach. SSRN Electronic Journal. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.757926
Santoso, R. A., & Handayani, A. (2019). Pengaruh Debt to Equity Ratio Terhadap Dividend Payout Ratio Melalui Return On Asset. Managerial, 6(2), 53. https://doi.org/10.30587/manajerial.v6i2.1013
APPENDIX
| Income Statement | |||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| Revenue from Contract with Customer Excluding Assessed Tax | 1326173 | 1402637 | 1387439 |
| Cost of Goods and Services Sold | 992655 | 1109072 | 1068480 |
| Gross Profit | 333518 | 293565 | 318959 |
| Selling General and Administrative Expense | 219234 | 226281 | 231111 |
| Operating Income Loss | 114284 | 67284 | 87848 |
| Other Operating Income Expense Net | -4404 | -8622 | -8098 |
| Income Loss from Continuing Operations Before Income Taxes Extraordinary Items Noncontrolling Interest | 109880 | 58662 | 79750 |
| Income Tax Expense Benefit | 30392 | 12968 | 17836 |
| Net Income Loss | 79488 | 45694 | 61914 |
Balance Sheet Statement |
|||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
| Assets | |||
| Assets Current | |||
| Cash and Cash Equivalents at Carrying Value | – | 17087 | 14952 |
| Restricted Cash and Cash Equivalents at Carrying Value | – | 12154 | 0 |
| Accounts Receivable Net Current | – | 192767 | 196806 |
| Inventory Net | – | 78344 | 71089 |
| Contract with Customer Asset Net Current | – | – | 73582 |
| Prepaid Expense and Other Assets Current | – | 16451 | 25481 |
Total Assets Current 公司财务代写 |
– | 371898 | 381910 |
| Property Plant and Equipment Net | – | 315823 | 324386 |
| Operating Lease Right of Use Asset | – | – | 52892 |
| Goodwill | – | 185832 | 185516 |
| Intangible Assets Net Excluding Goodwill | – | 148235 | 140191 |
| Other Assets Noncurrent | – | 46380 | 44096 |
| Assets | – | 1068168 | 1128991 |
| Liabilities and Stockholders Equity | |||
| Liabilities Current | |||
| Accounts Payable Current | – | 72219 | 69056 |
| Employee Related Liabilities Current | – | 41119 | 40119 |
| Contract with Customer Liability Current | – | – | 32696 |
| Operating Lease Liability Current | – | – | 11272 |
| Long Term Debt Current | – | – | 5400 |
| Other Liabilities Current | – | 83159 | 118314 |
| Total Liabilities Current | – | 227512 | 276857 |
| Long Term Debt Noncurrent | – | 245724 | 212500 |
| Operating Lease Liability Noncurrent | – | – | 43163 |
| Self Insurance Reserve Noncurrent | – | 21433 | 22831 |
| Other Liabilities Noncurrent | – | 77182 | 56862 |
Total Liabilities 公司财务代写 |
550418 | 612213 | |
| Stockholders Equity | |||
| Common Stock Value | – | 9005 | 8814 |
| Additional Paid-in Capital | – | 151842 | 154016 |
| Retained Earnings Accumulated Deficit | – | 367597 | 388010 |
| Common Stock Issued Employee Stock Trust | – | 755 | 685 |
| Deferred Compensation Liability Current and Noncurrent | – | 755 | 685 |
| Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income Loss Net of Tax | – | -32127 | -34062 |
| Stockholders Equity | – | 496317 | 516778 |
| Liabilities and Stockholders Equity | – | 1068168 | 1128991 |
| Cashflow Statement | |||
| 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | |
Net Cash Provided by Used in Operating Activities |
|||
| Net Income Loss | 79488 | 45694 | 61914 |
| Adjustments to Reconcile Net Income Loss to Cash Provided by Used in Operating Activities | |||
| Depreciation Depletion and Amortization | 54843 | 49798 | 46795 |
| Share-Based Compensation | 6200 | 6286 | 6600 |
| Deferred Income Tax Expense Benefit | 3195 | -5506 | 10463 |
| Gain Loss on Sale of Property Plant Equipment | -1037 | 2475 | 2197 |
| Impairment of Intangible Assets Indefinite lived Excluding Goodwill | 0 | 3141 | 0 |
| Proceeds from new markets tax credit transaction net of deferred costs | 0 | 8850 | 0 |
| Operating Lease Right of Use Asset Amortization | 0 | 0 | 12420 |
| Other Noncash Income Expense | 1431 | 2179 | 1516 |
| Increase Decrease in Operating Capital | |||
| Increase Decrease in Receivables | -18172 | -18164 | 4217 |
| Increase Decrease in Inventories | -10387 | -5114 | -7142 |
| Increase Decrease in Contract with Customer Asset | -1134 | 48712 | 18468 |
| Increase Decrease in Accounts Payable and Accrued Liabilities | -25627 | 7600 | -375 |
| Increase Decrease in Contract with Customer Liability | -16541 | 9026 | 11314 |
| Increase Decrease in Income Taxes Payable Net of Income Taxes Receivable | 315 | 3680 | -8726 |
| Increase Decrease Operating Lease Liabilities | 0 | 0 | 10829 |
| Increase Decrease in Other Operating Capital Net | 3714 | 2058 | 3065 |
| Net Cash Provided by Used in Operating Activities | 127463 | 96423 | 107262 |
Net Cash Provided by Used in Investing Activities 公司财务代写 |
|||
| Payments to Acquire Property Plant and Equipment | 53196 | 60717 | 51428 |
| Proceeds from Sale of Property Plant and Equipment | 1394 | 12333 | 5307 |
| Payments to Acquire Available for Sale Securities Debt | 10244 | 9213 | 7012 |
| Proceeds from Sale of Available for Sale Securities Debt | 10476 | 6110 | 7768 |
| Payments to Acquire Businesses Net of Cash Acquired | 182849 | 0 | 0 |
| Payments for Proceeds from Other Investing Activities | -851 | 2209 | 1673 |
| Net Cash Provided by Used in Investing Activities | -233568 | -53696 | -47038 |
| Net Cash Provided by Used in Financing Activities | |||
| Proceeds from Lines of Credit | 385700 | 363000 | 229000 |
| Proceeds from Term Loan Issuance | 0 | 0 | 150000 |
| Repayments of Lines of Credit | 235740 | 333000 | 406500 |
| Payments for Repurchase of Common Stock | 33676 | 43326 | 25140 |
| Amounts of Dividends Common Stock | 16393 | 17864 | 18714 |
| Proceeds from Payments for Other Financing Activities | -1557 | -1136 | -3160 |
| Net Cash Provided by Used in Financing Activities | 98334 | -32326 | -74514 |
| Cash Equivalents Restricted Cash and Restricted Cash Equivalents Period Increase Decrease Including Exchange Rate Effect | -7771 | 10401 | -14290 |
| Effect of Exchange Rate on Cash & Cash Equivalents Restricted Cash and Restricted Cash Equivalents | -167 | -519 | 1 |
| Cash & Cash Equivalents Restricted Cash and Restricted Cash Equivalents | – | 29241 | 14952 |




